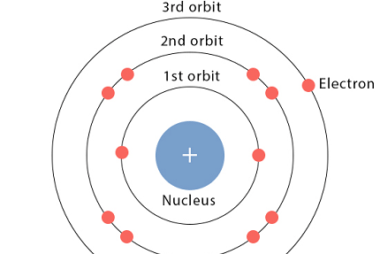
De Broglie hypothesis
The De Broglie hypothesis, proposed by French physicist Louis de Broglie in 1924, suggests that all matter, including particles such as electrons and protons, exhibits wave-like properties. According to the hypothesis, particles have both particle-like and wave-like characteristics, and the wavelength of these particles is inversely proportional to their momentum. This means that the more…