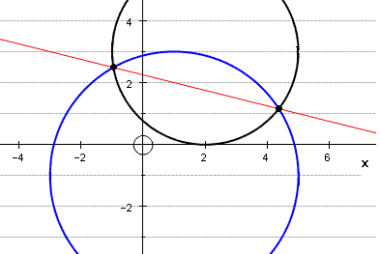
Equation of a circle through the points of intersection of two circles and Those of a circle and A straight line
To find the equation of a circle passing through the points of intersection of two circles, we can follow these steps: Let’s say the two circles have equations: (x – a)^2 + (y – b)^2 = r^2 (x – c)^2 + (y – d)^2 = s^2 where (a,b) and (c,d) are the centers of the…