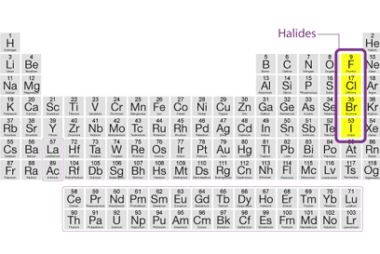
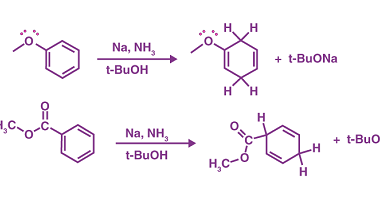
Halides
Halides are a class of chemical compounds that contain a halogen atom, such as fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine, bonded to a metal. These compounds are also known as salts, as they are formed by the reaction of a metal with a halogen. Halides can be classified as either ionic or covalent, depending on the…