Electronegativity
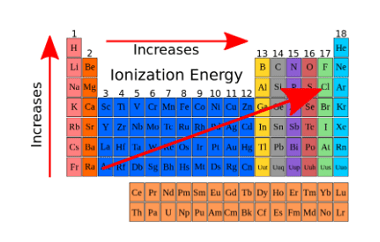
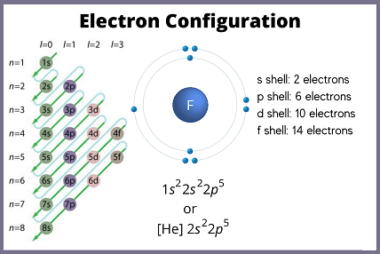
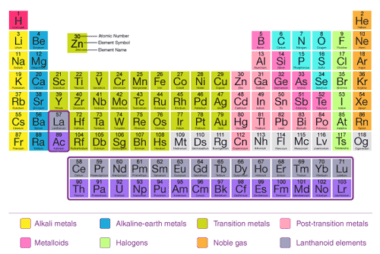
Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons towards itself. It is a relative property, which means that it is determined by comparing the electronegativities of different elements. The electronegativity of an element is determined by factors such as the nuclear charge, the number of electrons in…