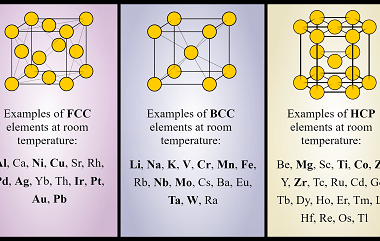
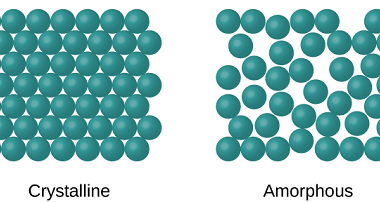
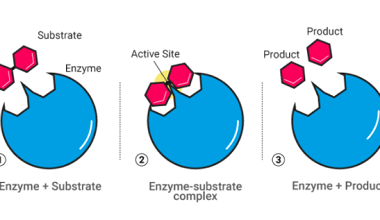
Nearest neighbours
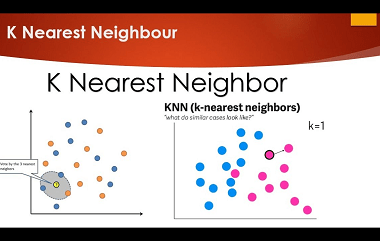
Nearest neighbors is a machine learning algorithm that is commonly used for classification and regression tasks. It works by finding the training examples in the training set that are closest to a given input example and using those examples to make a prediction. In the context of clustering, nearest neighbors refers to a method of…