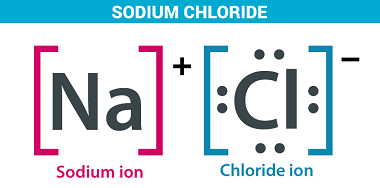
Sodium hydrogen carbonate
Sodium hydrogen carbonate, also known as sodium bicarbonate or baking soda, is a chemical compound with the molecular formula NaHCO3. It is a white crystalline powder that is soluble in water and has a slightly alkaline taste. Sodium hydrogen carbonate has a wide range of uses. It is commonly used as a leavening agent in…