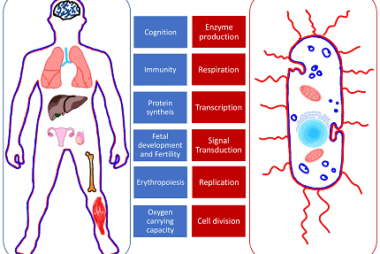
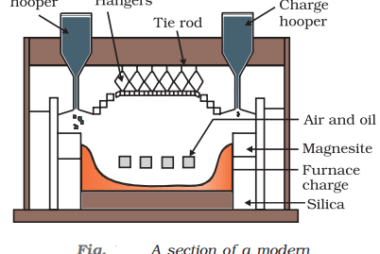
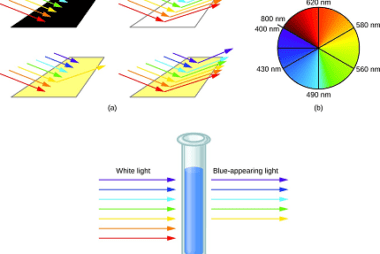
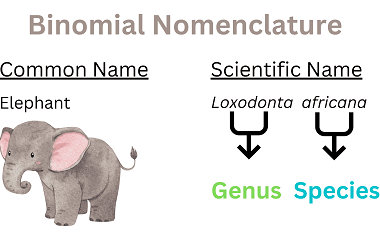
Halogenation
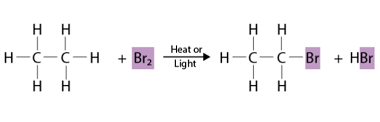
Halogenation refers to a chemical reaction in which a halogen atom (such as chlorine, bromine, or iodine) is introduced into a molecule. This can occur through several different types of reactions, including substitution, addition, and radical reactions. In a substitution reaction, a halogen atom replaces another atom or group of atoms in a molecule. For…