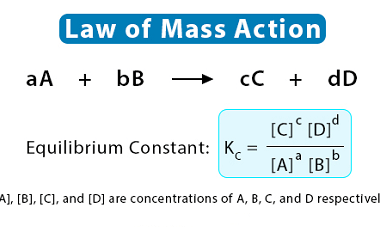
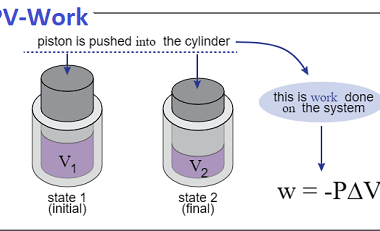
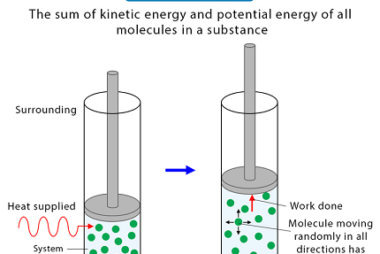
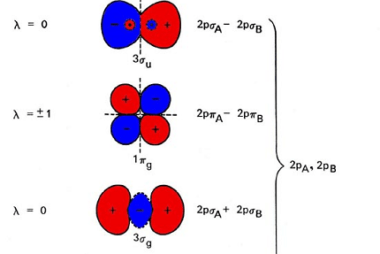
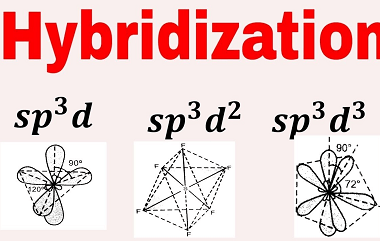
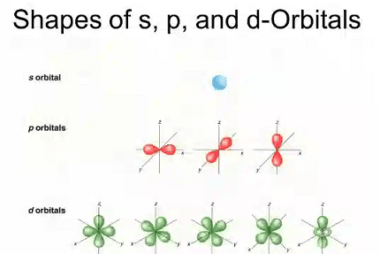
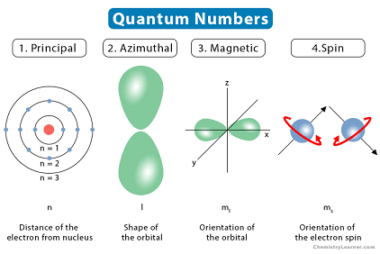
Law of mass action
The law of mass action is a fundamental principle in chemistry and chemical kinetics that describes the relationship between the concentrations of reactants and products in a chemical reaction at equilibrium. It states that the rate of a chemical reaction is proportional to the product of the concentrations of the reactants, each raised to a…