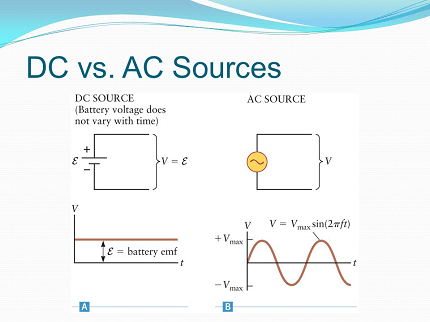
DC (direct current) and AC (alternating current) are two types of electrical power sources.
DC sources provide a steady and constant flow of electrical energy in one direction. Batteries, fuel cells, and photovoltaic cells are common examples of DC sources.
AC sources, on the other hand, provide electrical energy that alternates in direction and magnitude over time. AC power is what is delivered to homes and businesses by the power grid. AC sources are typically generated by rotating machines such as turbines or generators, which produce a changing magnetic field that induces a flow of electrons in a conductor.
The main difference between DC and AC sources is the way in which the electrical energy is delivered. DC power is constant, while AC power oscillates back and forth in a sinusoidal pattern. AC power is typically easier to transmit over long distances and is more efficient for powering motors and other devices that require a changing current. However, DC power is often used for electronics and other devices that require a constant voltage.
What is Required With d.c. and a.c. sources
To use DC and AC sources, different components and requirements are necessary:
For DC sources:
- DC power supply: to convert AC voltage from the wall outlet to DC voltage, or to regulate and provide a stable DC voltage output.
- Protection circuitry: to protect the circuit and the device from overvoltage, overcurrent, and short circuits.
- Filtering components: to reduce electrical noise and ripple in the DC output.
- Voltage regulators: to maintain a stable output voltage despite changes in load or input voltage.
- Energy storage devices: such as batteries or capacitors, to store electrical energy and provide backup power.
For AC sources:
- AC power source: such as a power plant or generator, to produce the AC voltage.
- Transformers: to step up or step down the voltage as needed for different applications and to isolate the AC source from the load.
- Circuit breakers and fuses: to protect against overcurrent and short circuits.
- Filters and capacitors: to reduce noise and harmonics in the AC signal.
- Power conditioning equipment: such as voltage stabilizers, surge protectors, and power factor correction devices, to ensure a stable and efficient power supply.
Both DC and AC sources can be used for a wide range of applications, from powering small electronic devices to operating large industrial machinery, depending on the specific requirements of the application.
When is Required With d.c. and a.c. sources
DC and AC sources are required in various applications, depending on the specific needs of the system. Here are some examples:
DC sources are commonly used for:
- Electronic devices: such as mobile phones, laptops, and personal computers.
- Automotive systems: such as the car battery, alternator, and motor controllers.
- Industrial control systems: such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and sensors.
- Renewable energy systems: such as solar panels and wind turbines.
- Telecommunications systems: such as power over Ethernet (PoE) and fiber optic networks.
AC sources are commonly used for:
- Home and office electricity: to power lighting, heating, air conditioning, and appliances.
- Industrial machinery: such as motors, pumps, and compressors.
- Electric power transmission: to deliver electrical energy over long distances from power plants to consumers.
- Electric vehicle charging: to charge the battery of an electric vehicle.
- Medical equipment: such as X-ray machines and MRI scanners.
In summary, DC and AC sources are required in a wide range of applications, from small electronic devices to large industrial machinery, depending on the specific requirements of the system.
Where is Required With d.c. and a.c. sources
DC and AC sources are required in many different locations, depending on the application. Here are some examples:
DC sources are commonly used in:
- Homes and offices: to power electronic devices such as computers, phones, and televisions.
- Automotive applications: to power the electrical systems of cars, trucks, and other vehicles.
- Industrial settings: to power control systems and sensors.
- Renewable energy systems: to convert and store energy from solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable sources.
- Telecommunications networks: to power network devices such as routers and switches.
AC sources are commonly used in:
- Homes and offices: to provide electricity for lighting, heating, air conditioning, and appliances.
- Industrial settings: to power machinery, motors, and other electrical systems.
- Power plants: to generate electricity for distribution to homes, businesses, and other locations.
- Electric vehicle charging stations: to charge the batteries of electric vehicles.
- Medical facilities: to power medical equipment such as X-ray machines and MRI scanners.
In summary, DC and AC sources are required in a variety of locations, from homes and offices to industrial facilities and power plants. The specific location will depend on the application and the specific requirements of the system.
How is Required With d.c. and a.c. sources
DC and AC sources are used in different ways depending on the application. Here are some examples of how they are used:
DC sources:
- Electronic devices: DC sources are used to power and charge electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets. The DC voltage is typically supplied by a battery or an AC to DC power adapter that plugs into a wall outlet. The battery can be recharged by connecting it to an AC source.
- Automotive systems: The DC battery in a car or truck provides power for the vehicle’s electrical systems, such as lights, radio, and air conditioning. The battery is charged by the alternator, which is driven by the engine.
- Industrial control systems: DC sources are used to power sensors, actuators, and other control devices in industrial automation systems. The DC voltage is typically supplied by a power supply or battery backup system.
- Renewable energy systems: DC sources are used to convert and store energy from renewable sources such as solar panels and wind turbines. The DC voltage is typically converted to AC voltage for distribution and use.
- Telecommunications networks: DC sources are used to power network devices such as routers and switches. The DC voltage is typically supplied by a power supply or battery backup system.
AC sources:
- Home and office electricity: AC sources are used to power lighting, heating, air conditioning, and appliances in homes and offices. The AC voltage is typically supplied by the power grid through a power outlet.
- Industrial machinery: AC sources are used to power motors, pumps, and other machinery in industrial settings. The AC voltage is typically supplied by a motor control system or a variable frequency drive.
- Power plants: AC sources are used to generate and distribute electricity to homes, businesses, and other locations. The AC voltage is typically generated by rotating machines such as turbines or generators.
- Electric vehicle charging stations: AC sources are used to charge the batteries of electric vehicles. The AC voltage is typically supplied by the power grid or a local generator.
- Medical facilities: AC sources are used to power medical equipment such as X-ray machines and MRI scanners. The AC voltage is typically supplied by a hospital-grade power supply.
In summary, DC and AC sources are used in different ways depending on the application, and the specific method of use will depend on the requirements of the system.
Production of With d.c. and a.c. sources
DC and AC sources can be produced in different ways, depending on the specific requirements of the application. Here are some examples of how they can be produced:
DC sources:
- Batteries: DC sources can be produced using batteries, which convert chemical energy into electrical energy. Batteries come in many different types, such as alkaline, lead-acid, lithium-ion, and nickel-cadmium.
- DC power supplies: DC sources can also be produced using DC power supplies, which convert AC voltage from the power grid into DC voltage. DC power supplies can also be used to regulate the voltage and current output, which is useful in many applications.
- Renewable energy sources: DC sources can be produced using renewable energy sources such as solar panels, which convert sunlight into electrical energy. Wind turbines can also be used to generate DC voltage.
AC sources:
- Power plants: AC sources are typically produced by power plants, which use rotating machines such as turbines or generators to produce AC voltage. Power plants can use different types of fuels, such as coal, natural gas, nuclear, or renewable sources such as hydroelectric or wind.
- AC generators: AC sources can also be produced using AC generators, which are often used in portable power generation systems or backup power systems. AC generators convert mechanical energy into AC voltage.
- Inverters: AC sources can also be produced using inverters, which convert DC voltage from batteries or renewable sources into AC voltage. Inverters can be used in solar power systems and other applications where DC voltage needs to be converted to AC voltage.
In summary, DC and AC sources can be produced using a variety of methods, depending on the specific requirements of the application. These include batteries, power plants, generators, power supplies, and inverters.
Case Study on With d.c. and a.c. sources
One case study of the use of DC and AC sources is in the field of renewable energy, specifically with solar power systems.
Solar power systems use DC sources to convert the energy from the sun into electricity. Solar panels are made up of photovoltaic (PV) cells, which convert sunlight into DC voltage. The DC voltage is then fed into an inverter, which converts it into AC voltage for use in homes or businesses.
One example of the use of solar power systems is in the city of San Francisco, which has set a goal to achieve 100% renewable energy by 2030. One way the city is working to achieve this goal is by installing solar panels on buildings and other structures throughout the city.
In one project, the San Francisco Public Utilities Commission (SFPUC) installed solar panels on the roof of the Sunset Reservoir, which is a large water storage facility. The solar panels generate DC voltage, which is then converted into AC voltage using inverters. The AC voltage is then fed into the power grid, where it is distributed to homes and businesses in the city.
The solar power system at the Sunset Reservoir has a capacity of 5 megawatts (MW), which is enough to power about 1,500 homes. The system is expected to generate about 7.2 million kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per year, which will reduce greenhouse gas emissions by about 6,000 metric tons annually.
Overall, the use of DC and AC sources in solar power systems is an example of how renewable energy can be used to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and move toward a more sustainable future. The San Francisco project is just one example of how solar power is being used to generate electricity in cities and communities around the world.
White paper on With d.c. and a.c. sources
Here is a white paper on the topic of DC and AC sources:
Introduction
DC (direct current) and AC (alternating current) sources are two different types of electrical power sources that are used in various applications. DC sources provide a constant voltage or current, while AC sources provide a voltage or current that oscillates in a sinusoidal waveform. In this white paper, we will explore the differences between DC and AC sources, the advantages and disadvantages of each, and their applications in different industries.
DC Sources
DC sources provide a constant voltage or current that does not change polarity or direction. DC sources can be produced using batteries, DC power supplies, and renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines. DC sources have the following advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Easy to control and regulate the voltage and current output
- Can be used to power devices that require a constant voltage or current, such as electronics and electric vehicles
- Efficient for long-distance power transmission
- Can be used in low voltage applications, such as powering small devices and circuits
Disadvantages:
- Difficult to transform the voltage level, which can limit the voltage range of DC sources
- Not suitable for high voltage applications, such as power grids and transmission lines
- Limited availability of renewable energy sources that produce DC voltage
AC Sources AC sources provide a voltage or current that oscillates in a sinusoidal waveform, changing polarity and direction periodically. AC sources can be produced using power plants, AC generators, and inverters. AC sources have the following advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Can be easily transformed to different voltage levels using transformers, allowing for high voltage power transmission over long distances
- Suitable for high voltage applications, such as power grids and transmission lines
- More widely available and produced at a larger scale, particularly through power plants
- Better for powering electric motors and devices that require alternating current
Disadvantages:
- Difficult to control and regulate the voltage and current output
- Less efficient for low voltage power transmission and for powering small devices and circuits
- Can cause electromagnetic interference (EMI) and noise in some applications
Applications
DC and AC sources are used in various industries and applications, depending on their specific advantages and disadvantages. Here are some examples:
- Automotive industry: DC sources are used to power electric vehicles and hybrid cars, while AC sources are used in charging stations and for powering electric motors.
- Telecommunications industry: DC sources are used to power network equipment and servers, while AC sources are used for powering larger telecommunications equipment and facilities.
- Renewable energy industry: DC sources are used in solar power systems and wind turbines, while AC sources are used in power plants and inverter systems.
Conclusion
DC and AC sources are two different types of electrical power sources that are used in various applications. They have different advantages and disadvantages, and are used in different industries depending on their specific characteristics. DC sources are typically used for low voltage applications and for powering devices that require a constant voltage or current, while AC sources are typically used for high voltage power transmission and for powering electric motors and devices that require alternating current. Understanding the differences between DC and AC sources is important for selecting the appropriate power source for specific applications.
