Phenols are a class of organic compounds that contain a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to an aromatic ring. They are important intermediates in many organic syntheses and have a wide range of applications in industry and medicine.
In the context of JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course, the study of phenols is typically covered in the section on organic chemistry. Some of the important topics related to phenols that are typically covered in the course include:
- Nomenclature of phenols
- Preparation of phenols through various methods such as electrophilic substitution, nucleophilic substitution, and hydrolysis of diazonium salts.
- Properties of phenols, such as acidity, basicity, solubility, and reactivity.
- Methods of synthesis of phenols and their derivatives.
- Reactions of phenols, such as electrophilic aromatic substitution, nucleophilic aromatic substitution, and addition reactions.
In addition to these topics, students may also study the application of phenols in the synthesis of important organic compounds such as aspirin, paracetamol, and salicylic acid.
Overall, the study of phenols is an important part of the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in organic chemistry, and a good understanding of their properties, reactions, and applications is essential for success in the exam.
History of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Phenols
The history of the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols can be traced back to the early development of organic chemistry as a field of study.
The discovery of phenol as a compound dates back to the early 19th century, when it was first isolated from coal tar by Friedrich Reichenbach. Over the next few decades, chemists such as August Wilhelm von Hofmann and Charles Friedel studied the properties and reactions of phenol, laying the foundation for its use as an important intermediate in organic syntheses.
The study of phenols continued to develop throughout the 20th century, as new methods for the synthesis and functionalization of phenols were developed. In the context of the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course, the study of phenols became an important part of the curriculum in the early years of the JEE exam, which was first introduced in India in 1960.
Over the years, the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols has evolved to keep pace with the latest developments in organic chemistry. Today, the course covers a wide range of topics related to phenols, including their synthesis, properties, reactions, and applications in industry and medicine.
Overall, the history of the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols is closely intertwined with the broader history of organic chemistry as a field of study, and reflects the ongoing evolution of our understanding of the properties and reactions of organic compounds.
Nature of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Phenols
The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols is a comprehensive study of the properties, reactions, and applications of this important class of organic compounds.
The course covers a wide range of topics related to phenols, including their nomenclature, preparation, properties, synthesis, and reactions. Students will learn about the different methods for preparing phenols, such as electrophilic substitution, nucleophilic substitution, and hydrolysis of diazonium salts.
The course also covers the properties of phenols, including their acidity, basicity, solubility, and reactivity. Students will learn about the factors that influence the acidity of phenols, such as the position of the hydroxyl group on the aromatic ring and the electron-withdrawing or electron-donating nature of substituents on the ring.
In addition, the course covers the different methods for synthesizing phenols and their derivatives, such as the Williamson ether synthesis and the Fries rearrangement. Students will also study the various reactions of phenols, such as electrophilic and nucleophilic aromatic substitution, and addition reactions.
Throughout the course, students will also learn about the applications of phenols in industry and medicine, including their use as starting materials in the synthesis of important organic compounds such as aspirin, paracetamol, and salicylic acid.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols is a comprehensive study of this important class of organic compounds, and is designed to provide students with a solid foundation in the principles and applications of organic chemistry.
Importance of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Phenols
The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols is of great importance to students pursuing a career in fields related to chemistry, such as chemical engineering, pharmaceuticals, and materials science. Some of the key reasons why the study of phenols is important in the context of JEE (Main+Advanced) are:
- Synthesis of important organic compounds: Phenols are important intermediates in the synthesis of many organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fragrances. The study of phenols provides students with a fundamental understanding of the principles and techniques involved in the synthesis of these compounds.
- Industrial applications: Phenols have a wide range of industrial applications, including their use in the production of resins, plastics, and adhesives. By studying phenols, students gain an understanding of the properties and reactivity of these compounds, which can be applied in the development of new materials and processes.
- Understanding of organic reactions: The study of phenols provides students with a deeper understanding of the principles of organic reactions, including electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution, and addition reactions. This knowledge can be applied to the study of other organic compounds, and is important for the development of new synthetic methods and the design of new materials.
- Preparation for advanced study: The study of phenols is an essential part of the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in organic chemistry, and provides students with a strong foundation in the principles and techniques of this important field. This knowledge is essential for success in advanced study and research in chemistry and related fields.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols is of great importance to students pursuing a career in chemistry or related fields, and provides a solid foundation in the principles and techniques of organic chemistry.
Benefits of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Phenols
The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols offers a range of benefits to students pursuing a career in fields related to chemistry. Some of the key benefits of studying phenols in the context of JEE (Main+Advanced) are:
- Strong foundation in organic chemistry: The study of phenols provides students with a solid foundation in the principles and techniques of organic chemistry. This knowledge is essential for success in advanced study and research in chemistry and related fields.
- Development of critical thinking skills: The study of phenols requires students to analyze and solve complex problems related to organic synthesis and reaction mechanisms. This helps to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills that are valuable in a range of careers.
- Preparation for advanced study and research: The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols provides students with the knowledge and skills needed to succeed in advanced study and research in chemistry and related fields. This includes the ability to design and carry out experiments, analyze data, and develop new synthetic methods.
- Career opportunities: Students who study phenols in the context of JEE (Main+Advanced) are prepared for careers in a wide range of fields, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, and chemical engineering. The knowledge and skills gained through the study of phenols are highly valued by employers in these industries.
- Contribution to society: The study of phenols has important implications for society, including the development of new medicines, materials, and technologies. Students who study phenols in the context of JEE (Main+Advanced) have the opportunity to contribute to these important areas of research and development.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols offers a range of benefits to students pursuing a career in chemistry or related fields, including a strong foundation in organic chemistry, the development of critical thinking skills, and preparation for advanced study and research.
Conclusion of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Phenols
In conclusion, the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols is an important and valuable component of the study of organic chemistry. The course provides students with a comprehensive understanding of the properties, reactions, and applications of phenols, which are important intermediates in the synthesis of a wide range of organic compounds.
By studying phenols, students gain a deeper understanding of the principles and techniques of organic chemistry, including electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution, and addition reactions. They also develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills that are essential for success in advanced study and research in chemistry and related fields.
The knowledge and skills gained through the study of phenols are highly valued by employers in a range of industries, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, and chemical engineering. Students who study phenols in the context of JEE (Main+Advanced) have the opportunity to make important contributions to these fields, and to society as a whole.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols is an essential part of the study of organic chemistry, and provides students with a solid foundation in the principles and techniques of this important field.
Overview of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Phenols
The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols is an important component of the study of organic chemistry. Phenols are aromatic compounds that contain a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to an aromatic ring. The study of phenols provides students with a comprehensive understanding of the properties, reactions, and applications of these compounds, which are important intermediates in the synthesis of a wide range of organic compounds.
The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols covers a range of topics, including the structure and properties of phenols, their reactions with electrophiles and nucleophiles, and their applications in the synthesis of organic compounds. Students also learn about the mechanism of reactions involving phenols, including the formation and reactions of phenoxide ions.
The course emphasizes the importance of experimental techniques in the study of phenols, including spectroscopic techniques such as UV-Vis and IR spectroscopy. Students learn how to design and carry out experiments involving phenols, and to analyze and interpret experimental data.
The knowledge and skills gained through the study of phenols in the context of JEE (Main+Advanced) are highly valued by employers in a range of industries, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, and chemical engineering. Students who study phenols in the context of JEE (Main+Advanced) are prepared for careers in these and other fields, and have the opportunity to make important contributions to research and development in these areas.
Types of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Phenols
The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols covers a variety of different types of phenols. Some of the major types of phenols covered in the course include:
- Monohydroxyphenols: These are phenols that contain a single hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to an aromatic ring. Examples include phenol, cresol, and xylenol.
- Dihydroxyphenols: These are phenols that contain two hydroxyl groups (-OH) attached to an aromatic ring. Examples include catechol, resorcinol, and hydroquinone.
- Trihydroxyphenols: These are phenols that contain three hydroxyl groups (-OH) attached to an aromatic ring. Examples include pyrogallol and phloroglucinol.
- Polyphenols: These are phenols that contain multiple hydroxyl groups (-OH) attached to multiple aromatic rings. Examples include tannins, flavonoids, and lignins.
The course also covers a range of derivatives and analogs of phenols, including halogenated phenols, nitrophenols, aminophenols, and alkylated phenols. Students learn about the properties, reactions, and applications of these different types of phenols, and how they can be synthesized and modified for specific purposes.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols provides students with a comprehensive understanding of the different types of phenols and their applications in organic synthesis and related fields.
Structures of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Phenols
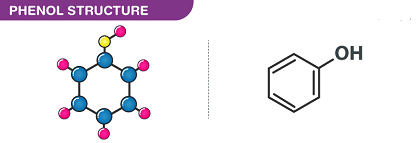
The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols covers a range of different structures of phenols, which are aromatic compounds that contain a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to an aromatic ring. The general structure of phenols is:
Ar-OH
where Ar represents an aromatic ring. The structure of phenol, which is the simplest and most commonly studied phenol, is:
C6H5OH
Other phenols can have different substitutions on the aromatic ring, giving rise to a range of different structures. Some examples of phenols covered in the course, along with their structures, include:
- Catechol:HO-C6H4-OH
- Resorcinol:HO-C6H4-OH
- Hydroquinone:HO-C6H4-OH
- Phenylphenol:C6H5-C6H4-OH
In addition to these basic structures, the course also covers different types of substituents on the aromatic ring, such as halogens, nitro groups, and alkyl groups. These substituents can have a significant effect on the properties and reactivity of phenols.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols provides students with a thorough understanding of the structures of different phenols and the impact of their structures on their properties and reactivity.
Nomenclature of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Phenols
The nomenclature of phenols is based on the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) rules for naming organic compounds. In general, phenols are named by adding the suffix “-ol” to the name of the parent aromatic hydrocarbon. For example, phenol, which is derived from benzene, is named as benzeneol.
When there are multiple substituents on the aromatic ring, the positions of the substituents are indicated by numbers, with the hydroxyl group (-OH) always being assigned the lowest possible number. For example, 2-methylphenol, also known as o-cresol, is named as such because the methyl group is attached to the second carbon atom on the ring, while the hydroxyl group is attached to the first carbon atom:
CH3 | CH3 | OH | C6H4
If there are multiple hydroxyl groups on the same aromatic ring, they are numbered consecutively, with the prefix “di-“, “tri-“, etc., indicating the number of hydroxyl groups. For example, 1,2-dihydroxybenzene, also known as catechol, is named as such because it contains two hydroxyl groups attached to adjacent carbon atoms on the benzene ring:
HO | HO | C6H4
In cases where there are substituents on both the hydroxyl group and the aromatic ring, the substituent on the ring is assigned a lower number than the substituent on the hydroxyl group. For example, 4-methyl-2-nitrophenol is named as such because the methyl group is attached to the fourth carbon atom on the ring, while the nitro group is attached to the second carbon atom on the ring, and the hydroxyl group is attached to the first carbon atom:
CH3 | NO2 | OH | C6H4
Overall, the nomenclature of phenols follows the same basic principles as the nomenclature of other organic compounds, with the position and nature of substituents on the aromatic ring and the hydroxyl group being used to determine the name of the compound.
Career Opportunities of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Phenols
A JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols can provide students with a strong foundation in organic chemistry and the properties and reactivity of phenols. This knowledge can be valuable for students interested in pursuing careers in a variety of fields, including:
- Chemical industry: Many companies in the chemical industry, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science, rely on organic chemistry knowledge to develop and manufacture products. Students who have completed a JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols may be well-suited for jobs in research and development or process chemistry.
- Academia: Students who complete an advanced course in phenols may be interested in pursuing further education in the field of organic chemistry or related areas, leading to a career in academia as a researcher or professor.
- Environmental science: Phenols are known environmental pollutants and are regulated by government agencies worldwide. Graduates with a JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols may be equipped to work for regulatory agencies, environmental consulting firms, or non-governmental organizations focused on environmental remediation and management.
- Patent law: Knowledge of organic chemistry, including phenols, can be valuable for careers in patent law. Patent attorneys help clients obtain patents for their inventions, and an understanding of organic chemistry can be particularly relevant for clients in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
Overall, a JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in phenols can open up a range of career opportunities in fields that rely on organic chemistry and chemical knowledge.
