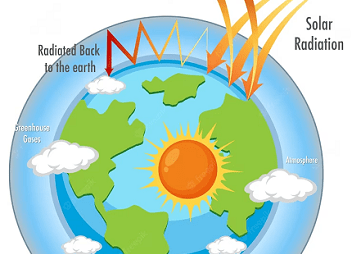
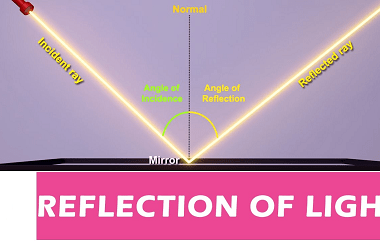
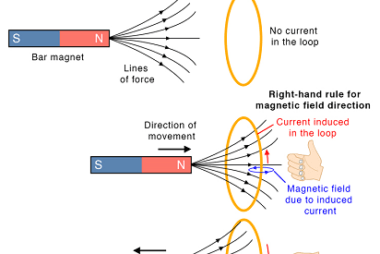
Integrated Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Types of solutions
Types of solutions In chemistry, solutions can be classified into various types based on different criteria. Here are some common types of solutions: Based on the state of the solute and solvent:a. Solid Solutions: These solutions involve a solid solute dissolved in a liquid or solid solvent. An example is an alloy like brass, which…