Cell Structure and Function is a fundamental topic in biology that explores the building blocks of life – cells – and their organization and activities. Here is a concise overview:
- Cell Theory: The cell theory states that all living organisms are composed of cells, and cells are the basic units of life.
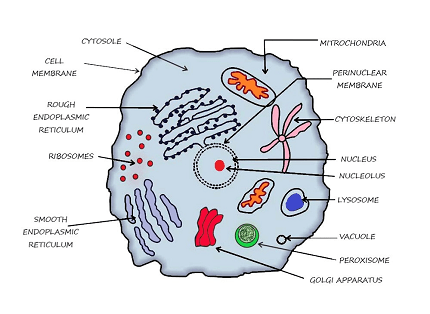
- Cell Components: Cells are composed of various components, including the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and organelles. The plasma membrane forms a barrier around the cell, regulating the movement of substances in and out. The cytoplasm contains the organelles and is where cellular processes occur.
- Organelles: Organelles are specialized structures within cells that carry out specific functions. Important organelles include the nucleus (stores genetic material), mitochondria (produce energy), endoplasmic reticulum (involved in protein synthesis), Golgi apparatus (modifies and packages molecules), and lysosomes (contain enzymes for digestion).
- Cell Membrane: The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that regulates the passage of substances in and out of the cell. It is selectively permeable, allowing the movement of certain molecules.
- Cell Division: Cells divide through processes like mitosis (for growth and tissue repair) and meiosis (for the production of gametes). Cell division ensures the transmission of genetic material and the formation of new cells.
- Cell Signaling: Cells communicate with each other through chemical signals. This involves receptor molecules on the cell surface, signal transduction pathways, and the activation of cellular responses.
- Cell Differentiation: Cells can differentiate and specialize into different types to perform specific functions in multicellular organisms. This process involves the activation or suppression of specific genes.
- Cellular Metabolism: Cells carry out various metabolic processes to sustain life. This includes cellular respiration (producing energy in the form of ATP) and photosynthesis (converting light energy into chemical energy).
- Cell Cycle: The cell cycle consists of stages (interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis) that regulate cell growth and division. Checkpoints ensure proper progression and prevent errors.
- Cell Genetics: Genetic information is stored in the form of DNA within the cell nucleus. DNA replication, transcription (RNA synthesis), and translation (protein synthesis) are vital processes for cell functioning and inheritance.
Understanding cell structure and function is crucial for comprehending biological processes at the cellular level and forms the basis for many advanced topics in biology.
The advanced course for NEET-AIIMS Biology covers the Cell Structure and Function topic in depth. It includes the study of various aspects related to cells, such as:
- Cell Theory: Understanding the fundamental principles of cell theory, which states that all living organisms are composed of cells, and cells are the basic units of life.
- Cell Components: Exploring the structure and function of different cell components, including the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, organelles (such as nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, etc.), and cytoskeleton.
- Cell Membrane: Examining the structure and functions of the cell membrane, including its selective permeability, transport mechanisms (such as diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, active transport), and cell signaling.
- Cell Organelles: Studying the functions and roles of major organelles within the cell, such as the nucleus (containing DNA and RNA), mitochondria (site of cellular respiration and ATP production), endoplasmic reticulum (involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism), Golgi apparatus (processing and packaging of molecules), lysosomes (cellular waste disposal), and peroxisomes (involved in detoxification).
- Cell Division: Understanding the process of cell division, including mitosis and meiosis, and their significance in growth, development, and reproduction.
- Cell Cycle: Exploring the stages of the cell cycle (interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis), regulation of the cell cycle, and the importance of checkpoints to ensure proper cell division.
- Cell Signaling and Communication: Investigating the mechanisms by which cells communicate with each other, including cellular receptors, signal transduction pathways, and the role of hormones and neurotransmitters.
- Cell Differentiation and Specialization: Examining how cells differentiate and specialize into various types to perform specific functions within multicellular organisms.
- Cell Metabolism: Introducing cellular metabolism, including an overview of cellular respiration, photosynthesis, and the production of ATP.
- Cell Genetics: Understanding the relationship between cells and genetics, including the structure and replication of DNA, RNA synthesis, protein synthesis (transcription and translation), and the role of genes in determining cell characteristics.
Throughout the advanced course, students will delve into advanced concepts and develop a comprehensive understanding of the intricate structure and functions of cells, preparing them for the NEET and AIIMS exams.
What is Required Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Biology Syllabus Cell Structure and Function
For the advanced course in NEET-AIIMS Biology, the syllabus for Cell Structure and Function typically includes the following topics:
- Cell Theory and Cell Types:
- Cell theory and its principles
- Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
- Plant and animal cells
- Comparison of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
- Cell Components and Organelles:
- Plasma membrane structure and functions
- Cytoplasm and its composition
- Nucleus: structure, functions, and nucleolus
- Mitochondria: structure, functions, and ATP production
- Endoplasmic reticulum: rough and smooth ER, protein synthesis
- Golgi apparatus: structure, functions, and protein modification
- Lysosomes: structure, functions, and intracellular digestion
- Peroxisomes: structure and functions
- Vacuoles and vesicles: structure and functions
- Ribosomes: structure and protein synthesis
- Cell Membrane and Transport:
- Fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane
- Lipid bilayer and membrane proteins
- Transport mechanisms: diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis
- Active transport and types of transport proteins
- Endocytosis and exocytosis
- Cell signaling and receptors
- Cell Division:
- Cell cycle: interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis
- Phases of mitosis: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
- Significance of mitosis in growth and tissue repair
- Meiosis and its importance in sexual reproduction
- Cell Differentiation and Specialization:
- Stem cells and their types
- Cell differentiation and developmental processes
- Tissues and their organization in multicellular organisms
- Cell Genetics:
- DNA structure and organization
- DNA replication and cell cycle checkpoints
- RNA synthesis: transcription and RNA processing
- Protein synthesis: translation and genetic code
- Cell Metabolism:
- Cellular respiration: glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain
- Photosynthesis: light-dependent and light-independent reactions
- ATP production and energy metabolism
These topics cover the essential aspects of cell structure and function necessary for the NEET-AIIMS Biology exam. It is advisable to consult the specific syllabus provided by the examination authorities for precise details and any updates.
When is Required Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Biology Syllabus Cell Structure and Function
The required advance course on the NEET-AIIMS Biology syllabus for Cell Structure and Function is typically covered during the preparatory period leading up to the NEET and AIIMS exams. The exact timing can vary depending on the curriculum followed by the educational institution or coaching center.
In general, the syllabus is covered over a span of several weeks or months, along with other topics in biology. The specific timeline and duration of the course may be determined by the teaching schedule and the pace of the curriculum.
It is important to check with your institution or coaching center for the precise schedule and duration of the advance course on Cell Structure and Function within the NEET-AIIMS Biology syllabus. They can provide you with the most accurate information regarding the timing and duration of the course.
Where is Required Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Biology Syllabus Cell Structure and Function
The required advance course on the NEET-AIIMS Biology syllabus, specifically covering Cell Structure and Function, is typically conducted in educational institutions, coaching centers, or online platforms that offer specialized NEET and AIIMS preparation courses.
These courses can be found in various cities and regions across India where NEET and AIIMS coaching is provided. Renowned coaching centers and institutions that focus on medical entrance exam preparation often offer comprehensive courses that cover all the topics included in the NEET and AIIMS syllabus, including Cell Structure and Function.
It is recommended to research and identify reputable coaching centers or online platforms that offer NEET and AIIMS preparation courses. You can consult with educational counselors, explore online resources, or seek recommendations from teachers, mentors, or fellow students who have previously undergone such courses.
Additionally, you can refer to the official websites of NEET and AIIMS for information about recognized coaching centers or online platforms that offer preparatory courses. These websites often provide guidance and resources for aspiring medical students.
It’s important to note that due to the evolving nature of education and technological advancements, online platforms and digital resources have become increasingly popular for NEET and AIIMS preparation, offering flexibility and accessibility to students across different locations.
How is Required Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Biology Syllabus Cell Structure and Function
The required advance course on the NEET-AIIMS Biology syllabus for Cell Structure and Function is designed to provide comprehensive knowledge and understanding of the topic. Here are some key features and aspects of the course:
- Curriculum Design: The course curriculum is carefully structured to cover all the essential aspects of Cell Structure and Function as per the NEET and AIIMS syllabus. It includes detailed study materials, lesson plans, and a logical progression of topics.
- Experienced Faculty: The course is taught by experienced and qualified faculty members who have expertise in the field of biology and a thorough understanding of the NEET and AIIMS exams. They guide students through the intricacies of cell structure and function, clarifying concepts and addressing queries.
- In-depth Theory: The course covers the theoretical aspects of cell structure and function, ensuring students have a strong foundation. It includes detailed explanations of cell components, organelles, cell membrane, cell division, cell signaling, cell differentiation, cellular metabolism, and cell genetics.
- Practical Sessions: Practical sessions and laboratory exercises may be included in the course to provide hands-on experience and reinforce the theoretical concepts. These sessions may involve microscopy, cell staining techniques, and observation of cell structures.
- Visual Aids and Illustrations: Visual aids such as diagrams, models, and illustrations are often utilized to enhance understanding and facilitate visualization of cellular structures and processes. These aids help students grasp complex concepts more effectively.
- Problem-solving and Application: The course may include problem-solving exercises and application-based questions to develop critical thinking skills and the ability to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios. This prepares students for the application-oriented questions that appear in the NEET and AIIMS exams.
- Practice Tests and Assessments: Regular practice tests and assessments are conducted to evaluate students’ understanding and provide them with opportunities to assess their progress. These tests may be modeled after the NEET and AIIMS exam patterns to familiarize students with the format and level of difficulty.
- Revision and Doubt Clearing: Dedicated revision sessions and doubt-clearing sessions are conducted to ensure that students have a thorough grasp of the topic. Students are encouraged to ask questions, clarify doubts, and reinforce their understanding through revision exercises.
- Study Resources: The course provides study resources such as textbooks, reference materials, and online resources to supplement classroom teaching and facilitate self-study.
- Mock Tests and Mock Exams: As the NEET and AIIMS exams approach, the course may include mock tests and mock exams that simulate the actual exam conditions. This helps students assess their preparedness, identify areas for improvement, and gain confidence in tackling the real exams.
The exact structure and delivery methods of the course can vary depending on the coaching center, institution, or online platform providing the course. It is recommended to research and choose a reputable and well-established institution or platform that offers quality NEET and AIIMS preparation courses.
Production of Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Biology Syllabus Cell Structure and Function
The production of an advanced course on the NEET-AIIMS Biology syllabus for Cell Structure and Function involves several steps and contributors. Here is a general overview of the production process:
- Curriculum Design: Experts in the field of biology and medical entrance exams collaborate to design the curriculum. They review the official NEET and AIIMS syllabus and determine the specific topics and subtopics to be covered in the course.
- Content Creation: Knowledgeable subject matter experts, including experienced biology faculty, develop the course content. This involves creating detailed lesson plans, lecture notes, study materials, and visual aids such as diagrams, illustrations, and animations.
- Review and Quality Assurance: The created content goes through a review process to ensure accuracy, clarity, and alignment with the NEET and AIIMS syllabus. This may involve multiple rounds of review by experts, faculty members, and curriculum developers.
- Lesson Delivery and Recording: The course content is then delivered by experienced faculty members. This can be done through classroom teaching or online platforms. In the case of online courses, the lectures may be recorded in video format to facilitate remote learning.
- Multimedia and Visual Enhancements: To enhance understanding and engagement, multimedia elements such as animations, simulations, and interactive activities may be incorporated into the course. These elements are designed to make complex concepts more accessible and memorable.
- Practical Sessions and Laboratory Exercises: If the course includes practical components, experts design practical sessions and laboratory exercises to provide hands-on learning experiences. These activities are carefully structured to reinforce theoretical concepts and develop practical skills.
- Assessment Development: A team of subject matter experts develops a range of assessment materials, including practice questions, quizzes, assignments, and mock tests. These assessments are designed to gauge students’ understanding, reinforce learning, and familiarize them with the NEET and AIIMS exam formats.
- Iterative Refinement: The course undergoes continuous refinement and improvement based on feedback from students, faculty, and subject matter experts. This ensures that the course remains up to date, aligned with the latest exam trends, and responsive to students’ needs.
- Publishing and Distribution: Once the course content is finalized, it is compiled into a comprehensive package. This may include textbooks, study guides, online course platforms, or other materials depending on the mode of delivery. The course is then made available to students through educational institutions, coaching centers, or online platforms.
It is important to note that the production process can vary depending on the institution or organization creating the course. Established coaching centers and educational publishers often have dedicated teams and a systematic approach to developing high-quality courses for NEET and AIIMS preparation.
Case Study on Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Biology Syllabus Cell Structure and Function
Certainly! Here’s a fictional case study that demonstrates the importance of understanding cell structure and function:
Case Study: Cell Structure and Cancer
Background: John, a 55-year-old male, visits his doctor complaining of persistent fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and a lump in his neck. Suspecting a potential health issue, the doctor orders several diagnostic tests, including a biopsy of the lump. The results reveal the presence of cancer cells.
Cell Structure Analysis: To better understand the nature of the cancer, the doctor examines the cell structure of the tumor. Using microscopy, they observe the following characteristics:
- Abnormal Cell Shape: The cancer cells exhibit irregular and enlarged shapes compared to normal cells. This is an indication of uncontrolled growth.
- Loss of Cell-to-Cell Adhesion: Cancer cells lack proper adhesion molecules, causing them to detach from neighboring cells. This enables their migration and invasion into surrounding tissues.
- Aberrant Nucleus: The nuclei of cancer cells appear larger, with irregular shapes and abnormal chromatin distribution. These nuclear changes signify genomic instability and altered gene expression.
- Increased Mitotic Rate: The presence of numerous cells in the process of division suggests a higher rate of cell division, which is a characteristic feature of cancer.
Implications of Cell Structure: The abnormal cell structure observed in the cancer cells has significant implications for disease progression and treatment:
- Metastasis: The loss of cell adhesion and increased mobility of cancer cells increase the likelihood of metastasis, where cancer cells spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system.
- Resistance to Apoptosis: Altered cell structure may confer resistance to programmed cell death (apoptosis). Cancer cells can evade normal cell death mechanisms, allowing them to survive and proliferate uncontrollably.
- Targeted Therapies: Understanding the unique features of cancer cell structure enables the development of targeted therapies. For instance, drugs that specifically disrupt abnormal cell adhesion or interfere with abnormal cell division can be employed to inhibit cancer growth.
- Prognosis and Treatment Planning: The cell structure analysis helps determine the severity and aggressiveness of the cancer. It aids in predicting disease progression, selecting appropriate treatment modalities, and monitoring response to therapy.
Conclusion: This case study highlights the importance of analyzing cell structure in the context of cancer. By examining cellular abnormalities, healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into disease behavior, guide treatment decisions, and develop personalized approaches for patients.
It is essential for medical professionals to have a strong understanding of cell structure and function to identify, characterize, and target abnormal cellular processes associated with diseases like cancer.
White paper on Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Biology Syllabus Cell Structure and Function
Title: Exploring Cell Structure and Function: A Comprehensive White Paper
Abstract: This white paper provides an in-depth exploration of cell structure and function, focusing on its significance in biological systems. The paper presents a comprehensive overview of the key components, organelles, and processes that contribute to the intricate functioning of cells. It highlights the fundamental role of cell structure in maintaining homeostasis, supporting cellular activities, and driving various physiological processes. Furthermore, the white paper examines the relevance of understanding cell structure and function in the context of medical research, disease mechanisms, and therapeutic interventions.
- Introduction
- Importance of Cell Structure and Function in Biology
- Historical Background and Milestones in Cell Structure Research
- Cell Theory and Cell Types
- Overview of Cell Theory and Its Significance
- Prokaryotic Cells: Structure and Functions
- Eukaryotic Cells: Structure and Functions
- Comparison of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
- Plasma Membrane
- Structure and Composition of the Plasma Membrane
- Functions: Cell Signaling, Selective Permeability, and Cell Adhesion
- Cellular Organelles
- Nucleus: Structure, Functions, and Genetic Control
- Mitochondria: Powerhouses of the Cell
- Endoplasmic Reticulum: Protein Synthesis and Lipid Metabolism
- Golgi Apparatus: Protein Modification and Sorting
- Lysosomes: Intracellular Digestion and Recycling
- Peroxisomes: Detoxification and Metabolism
- Vacuoles: Storage and Maintenance of Turgor Pressure
- Ribosomes: Protein Synthesis Machinery
- Cytoskeleton: Structure, Support, and Cellular Movement
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Overview of the Cell Cycle: Interphase and Mitotic Phase
- Phases of Mitosis: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase
- Significance of Cell Division in Growth, Development, and Tissue Repair
- Cell Signaling and Communication
- Overview of Cell Signaling Pathways
- Receptor-Mediated Signaling: Ligands, Receptors, and Signal Transduction
- Intracellular Signaling: Second Messengers and Protein Kinases
- Cell Differentiation and Specialization
- Stem Cells and their Role in Development and Regeneration
- Cellular Differentiation: Mechanisms and Significance
- Tissues and Organ Systems: Organization and Interactions
- Cell-Environment Interactions
- Cell Adhesion and Extracellular Matrix
- Cell-Cell Interactions: Gap Junctions, Tight Junctions, and Desmosomes
- Cell-Extracellular Matrix Interactions: Integrins and Focal Adhesions
- Cell Structure and Disease
- Aberrant Cell Structure in Disease: Cancer, Genetic Disorders, and Degenerative Conditions
- Impact of Altered Cell Structure on Cellular Function and Homeostasis
- Therapeutic Implications
- Targeting Cell Structure for Disease Treatment and Intervention
- Drug Delivery Systems and Strategies
- Emerging Technologies and Techniques in Cell Structure Analysis
- Conclusion
- Summary of Key Findings
- Future Perspectives and Areas of Research
This white paper serves as a comprehensive resource for researchers, educators, and healthcare professionals seeking a deeper understanding of cell structure and function. It provides a foundation for further exploration and highlights the potential impact of cell structure knowledge on various scientific and medical advancements.