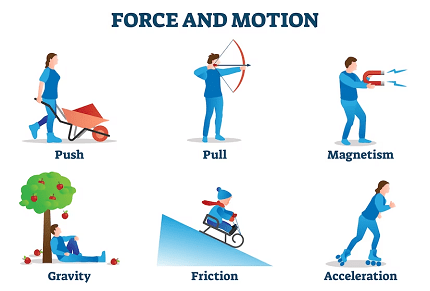
Certainly! Here’s a more detailed explanation of the Laws of Motion:
- Newton’s First Law of Motion (Law of Inertia): This law states that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will continue moving in a straight line with a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force. In simpler terms, an object resists any change in its state of motion. The inertia of an object refers to its tendency to maintain its current state.
- Newton’s Second Law of Motion: This law relates the net force acting on an object to its mass and acceleration. It can be mathematically expressed as F = ma, where F is the net force applied to an object, m is its mass, and a is the resulting acceleration. This law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force applied to it and inversely proportional to its mass.
- Newton’s Third Law of Motion (Law of Action and Reaction): According to this law, for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object simultaneously exerts a force of equal magnitude but in the opposite direction on the first object. This law illustrates that forces always occur in pairs.
These laws provide a framework for understanding the behavior of objects in motion and the forces acting upon them. They are fundamental to classical mechanics and have applications in various areas of physics and engineering.
Additional concepts related to the Laws of Motion include:
- Force: A force is a push or pull acting on an object that can cause it to accelerate or change its state of motion.
- Mass: Mass is a measure of the amount of matter present in an object. It is a scalar quantity and is typically measured in kilograms (kg).
- Acceleration: Acceleration refers to the rate at which an object’s velocity changes. It is a vector quantity measured in meters per second squared (m/s^2).
- Momentum: Momentum is the product of an object’s mass and velocity. It is a vector quantity and is given by the equation p = mv, where p represents momentum, m is mass, and v is velocity.
- Friction: Friction is a force that opposes the relative motion between two surfaces in contact. It acts in a direction opposite to the applied force and is influenced by factors such as the nature of the surfaces and the normal force.
- Equilibrium: An object is said to be in equilibrium when the net force acting on it is zero, resulting in a state of balanced forces. This can occur when an object is at rest or moving with a constant velocity.
It is essential to thoroughly understand these laws, concepts, and their applications, as they provide the foundation for studying various topics in mechanics and physics. Practice solving problems and working through examples to reinforce your understanding of these principles.
The Laws of Motion is an important topic in physics and forms the foundation of classical mechanics. It is a crucial part of the NEET-AIIMS physics syllabus. Here’s an overview of the Laws of Motion:
- Newton’s First Law of Motion (Law of Inertia): This law states that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will continue moving with a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force. In other words, an object will maintain its state of motion unless acted upon by an external force.
- Newton’s Second Law of Motion: This law relates the force acting on an object to its mass and acceleration. It can be stated mathematically as F = ma, where F represents the net force acting on the object, m is its mass, and a is the acceleration produced.
- Newton’s Third Law of Motion (Law of Action and Reaction): According to this law, for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. When an object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts a force of equal magnitude but in the opposite direction on the first object.
- Applications of Newton’s Laws: These laws have various applications, such as understanding the motion of objects on inclined planes, analyzing the motion of objects under the influence of frictional forces, and studying systems of connected objects (like pulleys and blocks).
- Impulse and Momentum: Impulse is defined as the change in momentum of an object when a force is applied to it for a certain period of time. Momentum is the product of an object’s mass and velocity. Newton’s laws can be used to analyze collisions and interactions between objects using the concepts of impulse and momentum.
- Circular Motion: Newton’s laws can also be applied to objects moving in circular paths. Concepts such as centripetal force, centripetal acceleration, and angular velocity are important in understanding circular motion.
It is crucial to have a strong conceptual understanding of these laws and their applications. Additionally, you should practice solving numerical problems related to these laws to reinforce your understanding and improve your problem-solving skills.
Note: It is important to consult the official syllabus and study materials provided by the organizing bodies of NEET and AIIMS to ensure you are fully aware of the specific topics and subtopics included in the physics syllabus for these exams.
What is Required Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus Laws of Motion
The Laws of Motion form an essential part of the NEET-AIIMS physics syllabus. While the exact syllabus may vary slightly each year, the following topics related to the Laws of Motion are typically included:
- Newton’s First Law of Motion:
- Definition and explanation of inertia.
- Examples illustrating the concept of inertia.
- Application of the first law in different scenarios.
- Newton’s Second Law of Motion:
- The relationship between force, mass, and acceleration (F = ma).
- Calculation of acceleration, force, or mass in given scenarios.
- Application of the second law to analyze different situations involving forces and motion.
- Newton’s Third Law of Motion:
- Explanation of action-reaction pairs.
- Examples demonstrating the application of the third law.
- Analyzing the effects of action-reaction forces on objects.
- Frictional Forces:
- Different types of friction (static and kinetic friction).
- Understanding the factors affecting frictional forces.
- Calculating frictional forces and their impact on objects in motion.
- The role of friction in various contexts, such as walking, driving, or sliding.
- Circular Motion:
- Centripetal force and centripetal acceleration in circular motion.
- Applying the laws of motion to analyze objects moving in circular paths.
- Understanding the concept of banking of roads and circular motion in vertical circles.
- Applications of Newton’s Laws:
- Resolving forces in inclined planes.
- Analyzing pulleys and connected systems.
- Understanding the concept of terminal velocity.
- Applications of the laws of motion in projectile motion.
These are the core topics related to the Laws of Motion that are typically covered in the NEET-AIIMS physics syllabus. It’s important to refer to the official syllabus and study materials provided by the organizing bodies of NEET and AIIMS for the most accurate and up-to-date information on the specific subtopics and depth of understanding required.
When is Required Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus Laws of Motion
The Laws of Motion, being a fundamental concept in physics, are an integral part of the NEET-AIIMS physics syllabus. The specific timing or schedule for when these topics are covered can vary depending on the curriculum followed by different coaching institutes or schools. However, in general, Laws of Motion are typically taught in the earlier stages of the physics curriculum.
It is recommended to consult the official syllabus and study materials provided by the organizing bodies of NEET and AIIMS to get precise information on the order and timing of topics. These materials will provide you with a detailed breakdown of the physics syllabus, including Laws of Motion, and the respective weightage given to each topic in the exams.
Additionally, it is advisable to follow a structured study plan and allocate sufficient time to understand the Laws of Motion thoroughly. You should aim to have a strong conceptual understanding of the laws and their applications, as they serve as the foundation for many other topics in physics. It is also crucial to practice solving numerical problems and applying the laws to various scenarios to enhance your problem-solving skills.
Where is Required Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus Laws of Motion
The Laws of Motion, as part of the NEET-AIIMS physics syllabus, can be found in various study materials and resources designed specifically for these exams. Here are some common sources where you can find the required advanced course NEET-AIIMS Physics syllabus on Laws of Motion:
- Official NEET and AIIMS Websites: The official websites of NEET (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test) and AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) provide detailed information about the syllabus and exam patterns. You can refer to these websites for the official syllabus, which will include the Laws of Motion.
- NCERT Textbooks: The NCERT (National Council of Educational Research and Training) Physics textbooks for classes 11 and 12 cover the Laws of Motion in a comprehensive manner. These textbooks are widely used and are considered an important resource for NEET and AIIMS preparation.
- Reference Books: There are various reference books available in the market that cater specifically to the NEET and AIIMS physics syllabus. These books often provide detailed explanations, practice questions, and solved examples related to the Laws of Motion. Some popular books include those written by HC Verma, DC Pandey, and Resnick Halliday.
- Online Study Platforms and Coaching Materials: Numerous online study platforms and coaching institutes offer comprehensive study materials, video lectures, and practice tests specifically designed for NEET and AIIMS preparation. These resources often cover the Laws of Motion in detail and provide ample practice questions and solutions.
- Previous Year Question Papers: Going through previous year question papers of NEET and AIIMS can give you an idea of the types of questions that have been asked on the Laws of Motion in the past. This will help you understand the level of difficulty and the specific topics that are frequently tested.
Remember to always refer to the official syllabus and study materials provided by the organizing bodies of NEET and AIIMS to ensure that you cover all the necessary topics in the Laws of Motion for the exams.
How is Required Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus Laws of Motion
The required advanced course NEET-AIIMS Physics syllabus for Laws of Motion is typically taught through a combination of theoretical explanations, examples, and problem-solving practice. Here’s an outline of how the Laws of Motion are covered in the syllabus:
- Theoretical Concepts: The Laws of Motion are introduced by explaining Newton’s three laws in detail. Each law is discussed, defining the key concepts and principles involved. The focus is on developing a strong conceptual understanding of these laws.
- Illustrative Examples: After introducing each law, illustrative examples are provided to demonstrate the application of the law in real-world scenarios. These examples help students visualize how the laws operate and understand their practical implications.
- Derivations and Mathematical Formulations: The mathematical formulations of the laws are derived and explained. The relationship between force, mass, and acceleration (Newton’s Second Law) is mathematically derived and related to real-life situations. This helps students grasp the quantitative aspects of the laws.
- Problem-Solving Practice: Students are given ample opportunities to solve numerical problems related to the Laws of Motion. These problems require the application of the laws to various situations, such as finding forces, accelerations, or masses. Solving problems helps students gain proficiency in using the laws and enhances their problem-solving skills.
- Applications and Advanced Topics: The syllabus may include the application of the Laws of Motion in different contexts, such as circular motion, friction, equilibrium, and connected systems. Advanced topics like torque, rotational motion, and momentum may also be covered to further explore the applications of the laws.
- Revision and Practice Tests: Regular revision sessions and practice tests are conducted to reinforce the understanding of the Laws of Motion. These sessions help students consolidate their knowledge, identify areas that need improvement, and build confidence for the exams.
It is important to note that the specific teaching methods and order of topics may vary among different institutions or coaching centers. It is advisable to follow the study materials and guidance provided by your teachers or coaching institute, as they are familiar with the NEET-AIIMS syllabus and can provide targeted instruction based on the exam requirements.
Structures of Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus Laws of Motion
The advanced course NEET-AIIMS Physics syllabus for Laws of Motion typically follows a structured approach to cover the required topics. Although the exact structure may vary depending on the teaching institution or coaching center, here is a general outline of the topics covered in the syllabus:
- Introduction to Laws of Motion:
- Definition of motion, force, and inertia.
- Overview of Newton’s three laws of motion.
- Newton’s First Law of Motion:
- Definition of inertia and its implications.
- Examples illustrating the concept of inertia.
- Application of the first law in different scenarios.
- Newton’s Second Law of Motion:
- Definition and mathematical formulation of the second law (F = ma).
- Calculation of acceleration, force, or mass in given scenarios.
- Application of the second law to analyze different situations involving forces and motion.
- Newton’s Third Law of Motion:
- Explanation of action-reaction pairs.
- Examples demonstrating the application of the third law.
- Analyzing the effects of action-reaction forces on objects.
- Frictional Forces:
- Different types of friction (static and kinetic friction).
- Understanding the factors affecting frictional forces.
- Calculating frictional forces and their impact on objects in motion.
- Application of friction in various contexts, such as walking, driving, or sliding.
- Circular Motion:
- Centripetal force and centripetal acceleration in circular motion.
- Applying the laws of motion to analyze objects moving in circular paths.
- Understanding the concept of banking of roads and circular motion in vertical circles.
- Applications of Newton’s Laws:
- Resolving forces in inclined planes.
- Analyzing pulleys and connected systems.
- Understanding the concept of terminal velocity.
- Applications of the laws of motion in projectile motion.
- Momentum and Collisions:
- Definition and calculation of momentum.
- Impulse and its relationship with momentum.
- Conservation of momentum in collisions.
- Additional Concepts:
- Equilibrium of forces.
- Torque and rotational motion.
- Rotational equilibrium and moment of inertia.
The syllabus structure may include periodic assessments, practice problems, and revision sessions to reinforce understanding and enhance problem-solving skills. It is essential to refer to the official syllabus and study materials provided by the organizing bodies of NEET and AIIMS, as they may provide additional details and specifications for the Laws of Motion syllabus.
Case Study on Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus Laws of Motion
Certainly! Let’s take a look at a case study on the advanced course NEET-AIIMS Physics syllabus specifically focusing on the Laws of Motion.
Case Study: Analyzing Projectile Motion
One of the key applications of the Laws of Motion is in understanding projectile motion. Let’s consider the case of a ball being thrown horizontally off a cliff.
- Problem Statement: A ball is thrown horizontally with an initial velocity of 10 m/s from the top of a cliff that is 20 meters high. Calculate: a) The time taken for the ball to reach the ground. b) The horizontal distance traveled by the ball before hitting the ground.
- Solution: To solve this problem, we can break it down into two components: horizontal motion and vertical motion.
a) Horizontal Motion: Since the ball is thrown horizontally, there is no initial vertical velocity. Therefore, the ball will continue to move horizontally with a constant velocity throughout its motion. The horizontal distance traveled by the ball can be calculated using the formula: distance = velocity × time. In this case, the horizontal velocity is 10 m/s, and the time taken is the same as the time taken for the ball to fall vertically.
b) Vertical Motion: The ball experiences vertical motion due to the force of gravity. The ball’s initial vertical position is 20 meters above the ground. Using the equation of motion for vertical motion: displacement = initial velocity × time + (1/2) × acceleration × time^2, we can find the time taken for the ball to reach the ground.
Given: Initial vertical velocity (uy) = 0 m/s (as the ball is thrown horizontally) Vertical displacement (sy) = -20 m (negative sign indicates downward direction) Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 9.8 m/s^2
Using the equation: sy = uy × t + (1/2) × g × t^2, we can solve for time (t) to reach the ground.
-20 = 0 × t + (1/2) × 9.8 × t^2 -10t^2 = -20 t^2 = 2 t = √2 ≈ 1.41 s
- Results: a) The time taken for the ball to reach the ground is approximately 1.41 seconds. b) The horizontal distance traveled by the ball is given by distance = velocity × time = 10 m/s × 1.41 s ≈ 14.1 meters.
- Conclusion: In this case study, we applied the Laws of Motion to analyze projectile motion. By breaking down the motion into horizontal and vertical components, we calculated the time taken for the ball to reach the ground and the horizontal distance traveled. This demonstrates the practical application of the Laws of Motion in understanding and solving problems related to projectile motion.
Remember, practicing similar case studies and solving problems related to the Laws of Motion will help you develop a deeper understanding of the subject and improve your problem-solving skills for NEET-AIIMS Physics.
White paper on Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus Laws of Motion
Title: Laws of Motion: Fundamentals, Applications, and Implications
Abstract: This white paper provides a comprehensive analysis of the Laws of Motion, exploring their fundamental principles, practical applications, and significant implications in the field of physics. The paper aims to deepen the understanding of these laws and their relevance in various contexts, including the NEET-AIIMS Physics syllabus. By examining the historical development of the laws and delving into their mathematical formulations, this white paper serves as a valuable resource for students, educators, and researchers in the field.
- Introduction:
- Background on the Laws of Motion and their significance in physics.
- Overview of the three laws and their historical context.
- Importance of understanding the Laws of Motion in scientific study and problem-solving.
- Newton’s First Law of Motion:
- Definition of inertia and its role in the first law.
- Examples illustrating the concept of inertia.
- Practical applications and implications of the first law in everyday life and scientific research.
- Newton’s Second Law of Motion:
- Mathematical formulation of the second law (F = ma).
- Understanding the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration.
- Applications of the second law in analyzing various forces and motion scenarios.
- Newton’s Third Law of Motion:
- Explanation of action-reaction pairs and their significance.
- Demonstrations and examples showcasing the application of the third law.
- Understanding the conservation of momentum and its connection to the third law.
- Frictional Forces:
- Introduction to different types of friction (static and kinetic).
- Factors affecting frictional forces and their measurement.
- Analysis of frictional forces in different contexts and their practical implications.
- Circular Motion and Universal Gravitation:
- Centripetal force and centripetal acceleration in circular motion.
- Applying the Laws of Motion to analyze objects in circular paths.
- Relationship between the Laws of Motion and the law of universal gravitation.
- Advanced Topics and Applications:
- Equilibrium of forces and resolving forces in different scenarios.
- Torque, rotational motion, and the laws of motion in rotational systems.
- Applications of the laws in projectile motion, collisions, and momentum conservation.
- Conclusion:
- Summary of the fundamental concepts and principles covered in the Laws of Motion.
- Importance of understanding and applying the laws in various scientific fields.
- Significance of the Laws of Motion in the NEET-AIIMS Physics syllabus and related examinations.
- References:
- Citations of primary sources, research papers, textbooks, and other relevant resources.
Please note that this white paper is a generalized outline and can be expanded upon with more detailed explanations, illustrations, and examples. It provides a solid starting point for understanding the Laws of Motion comprehensively and their significance in the NEET-AIIMS Physics syllabus.
