Bound charges
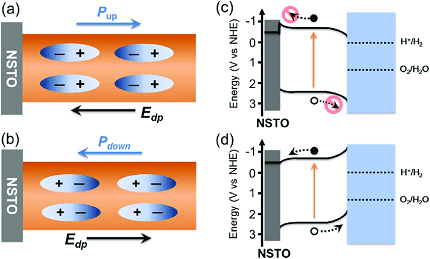
Bound charges refer to electric charges that are bound within a material and cannot move freely. They are often associated with the polarization of dielectric materials in the presence of an electric field. When an external electric field is applied to a dielectric material, the atoms or molecules in the material can become polarized.
Polarization occurs when the positive and negative charges within the atoms or molecules are separated, creating regions of positive and negative charge within the material. These separated charges are known as bound charges because they are bound to the atoms or molecules and cannot move independently.
The presence of bound charges leads to the formation of an internal electric field within the dielectric material. This internal electric field opposes the external electric field, reducing the overall electric field strength inside the dielectric.
The concept of bound charges is important in understanding the behavior of dielectric materials in various applications, such as capacitors. When a dielectric is inserted between the plates of a capacitor, the bound charges play a role in increasing the capacitance of the system. The bound charges contribute to the overall polarization of the dielectric, leading to an increase in the amount of stored electric charge.
In summary, bound charges are charges that are bound within a material and cannot move freely. They are associated with the polarization of dielectric materials in response to an external electric field and play a significant role in various electrical phenomena.
The Physics syllabus for the integrated course at AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) typically covers various topics related to the field of physics. While the specific syllabus may vary over time, here is a general overview that includes the concept of bound charges:
- Electrostatics:
- Coulomb’s law and electric field
- Gauss’s law and its applications
- Electric potential and potential difference
- Capacitance and capacitors
- Dielectrics and polarization
- Bound charges and their significance
The concept of bound charges is closely related to the behavior of dielectrics (insulating materials) in the presence of an electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, its atoms or molecules become polarized. This polarization leads to the separation of positive and negative charges within the material, creating what are known as bound charges.
Bound charges are different from free charges, which are charges that can move freely within a material. Bound charges, on the other hand, remain fixed within the dielectric and cannot move. They are responsible for the creation of an electric field inside the dielectric, which interacts with the external electric field.
The study of bound charges is important in various aspects of physics, including the behavior of capacitors with dielectric materials, the formation of electric dipoles, and the overall understanding of electric fields in different media.
It’s worth noting that this overview is a general description, and the specific depth of coverage on bound charges may vary depending on the curriculum and syllabus updates at AIIMS. It’s always recommended to refer to the latest official syllabus or consult with the institution for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
What is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Bound charges
Bound charges refer to electric charges that are confined or localized within a material. They are a result of the polarization of a dielectric material when it is subjected to an external electric field. When an electric field is applied to a dielectric, the atoms or molecules in the material can undergo polarization, causing the separation of positive and negative charges within the material.
The separation of charges leads to the formation of regions of positive and negative charge within the dielectric, creating electric dipoles. These dipoles are responsible for the generation of an internal electric field, which opposes the applied external electric field.
The charges associated with these dipoles are called bound charges because they are bound or fixed within the dielectric material and cannot move freely. They are typically localized around the individual atoms or molecules and do not contribute to the flow of electric current.
Bound charges play a significant role in various electrical phenomena, especially in the behavior of capacitors with dielectric materials. When a dielectric is inserted between the plates of a capacitor, the bound charges contribute to the overall polarization of the dielectric and increase its capacitance.
Understanding the concept of bound charges is crucial in analyzing the behavior of dielectric materials, the formation of electric dipoles, and the interaction between electric fields and dielectrics in different applications.
When is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Bound charges
Bound charges occur when a dielectric material undergoes polarization in the presence of an external electric field. When an electric field is applied to a dielectric, the atoms or molecules within the material experience a force that causes their charge distributions to shift. This shift leads to the separation of positive and negative charges within the material.
The separated charges within the dielectric material are referred to as bound charges. These charges are bound or confined within the material and cannot move freely. They remain fixed in their respective positions relative to the atoms or molecules.
The presence of bound charges within a dielectric material results in the formation of an internal electric field. This internal field opposes the applied external electric field, leading to a reduction in the overall electric field strength inside the dielectric.
Bound charges play a significant role in various electrical phenomena involving dielectric materials, such as the behavior of capacitors, the formation of electric dipoles, and the interaction between electric fields and dielectrics.
It’s important to note that bound charges are specific to dielectric materials and their response to external electric fields. Conducting materials, on the other hand, do not exhibit bound charges as their charges are free to move throughout the material.
Where is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Bound charges
Bound charges are found within dielectric materials when they are subjected to an external electric field. Dielectric materials are insulating materials that do not conduct electric current easily. When an electric field is applied to a dielectric material, its atoms or molecules undergo polarization.
The bound charges are localized within the dielectric material. They are associated with the separation of positive and negative charges within the material due to polarization. The positive bound charges are typically located closer to the negative end of the dipole, while the negative bound charges are closer to the positive end of the dipole.
It’s important to note that bound charges do not move freely within the dielectric material. They are fixed or bound to the atoms or molecules and do not contribute to the flow of electric current. Instead, they contribute to the creation of an internal electric field within the dielectric, which interacts with the applied external electric field.
The behavior and distribution of bound charges within a dielectric material depend on the characteristics of the material, such as its dielectric constant and the strength of the applied electric field.
Overall, bound charges are located within dielectric materials and play a crucial role in the response of the material to external electric fields.
How is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Bound charges
The presence of bound charges in a dielectric material is determined by the polarization of the material in response to an external electric field. When an electric field is applied to a dielectric, the atoms or molecules within the material may undergo a rearrangement of their charges, leading to the separation of positive and negative charges.
The process of polarization involves the displacement of the positive and negative charges within the atoms or molecules. This displacement gives rise to regions of positive and negative charge, creating electric dipoles within the material. The charges associated with these dipoles are the bound charges.
The magnitude and distribution of bound charges depend on factors such as the strength of the external electric field and the properties of the dielectric material, including its dielectric constant and molecular structure.
The bound charges are “required” in the sense that they are an inherent consequence of the polarization of the dielectric material. They are necessary for the dielectric to generate an internal electric field that counteracts the external electric field. This opposing internal electric field reduces the overall electric field strength within the dielectric.
The presence of bound charges is important for various electrical phenomena involving dielectric materials, such as increasing the capacitance of capacitors and influencing the behavior of insulating materials in the presence of electric fields.
In summary, bound charges are “required” as they are an essential aspect of the polarization process in dielectric materials and contribute to the response of the material to an external electric field.
Structures of AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Bound charges
The syllabus for the topic of bound charges may include the following subtopics:
- Coulomb’s law and electric field
- Gauss’s law and its applications
- Electric potential and potential difference
- Capacitance and capacitors
- Dielectrics and polarization
- Bound charges and their significance
These subtopics provide a foundation for understanding the behavior of charges, electric fields, and dielectric materials in the presence of an electric field. The specific depth of coverage and the organization of these topics within the AIIMS Physics syllabus may vary.
To obtain the most accurate and up-to-date information on the AIIMS Physics syllabus and the structures related to bound charges, it is recommended to refer to the official AIIMS website or contact the institution directly. They can provide you with the detailed syllabus and any specific structures or subtopics related to bound charges that are included in the curriculum.
Case Study on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Bound charges
Certainly! Let’s consider a case study on the topic of bound charges involving a capacitor with a dielectric material.
Case Study: Capacitor with Dielectric Material
Scenario: You have a parallel-plate capacitor with two conducting plates separated by a distance d. The capacitor is filled with a dielectric material. An external voltage source is connected to the plates, creating an electric field between them.
Objective: Investigate the behavior of bound charges in the dielectric material and their impact on the capacitance of the system.
Procedure:
- Setup:
- Place the dielectric material between the parallel plates of the capacitor.
- Apply an external voltage source to establish an electric field between the plates.
- Polarization and Bound Charges:
- When the electric field is applied, the dielectric material undergoes polarization.
- The positive and negative charges within the dielectric material separate, creating electric dipoles.
- The positive bound charges accumulate near the negative plate, while the negative bound charges accumulate near the positive plate.
- These bound charges are localized within the dielectric material and cannot move freely.
- Electric Field Distribution:
- The presence of bound charges within the dielectric material creates an internal electric field that opposes the external electric field.
- The internal electric field reduces the overall electric field strength within the dielectric.
- As a result, the electric field between the plates of the capacitor is weaker in the presence of the dielectric material compared to in a vacuum.
- Capacitance and Bound Charges:
- The presence of bound charges affects the capacitance of the system.
- Bound charges increase the polarization of the dielectric material, which enhances its ability to store electric charge.
- The increased polarization leads to an increase in the capacitance of the capacitor with the dielectric material compared to in a vacuum.
- Calculation and Analysis:
- Calculate the capacitance of the capacitor using the appropriate formula that considers the presence of the dielectric material.
- Compare the capacitance of the capacitor with the dielectric material to the capacitance of the capacitor without the dielectric material.
- Analyze the impact of the bound charges on the capacitance and the ability of the system to store electric charge.
Conclusion: In this case study, we investigated the behavior of bound charges in a capacitor with a dielectric material. We observed that the dielectric material undergoes polarization, resulting in the formation of bound charges. The presence of bound charges increases the polarization and enhances the ability of the system to store electric charge, leading to an increase in the capacitance of the capacitor. The understanding of bound charges is crucial for analyzing the behavior of dielectric materials and their impact on electrical systems.
White paper on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Bound charges
Title: Understanding Bound Charges: A Comprehensive White Paper
Abstract: This white paper aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of bound charges, a fundamental concept in electromagnetism and the behavior of dielectric materials. Bound charges play a crucial role in various electrical phenomena, such as the polarization of dielectrics, the behavior of capacitors, and the interaction between electric fields and insulating materials. This paper explores the definition, formation, properties, and significance of bound charges, providing insights into their contribution to the behavior of dielectrics in different applications. Additionally, the paper discusses experimental techniques, theoretical models, and mathematical formulations used to study and analyze bound charges. The information presented in this white paper is intended to serve as a valuable resource for researchers, educators, and students in the field of electromagnetism and related disciplines.
- Introduction
- Importance of bound charges in electromagnetism
- Overview of dielectric materials and their polarization
- Definition and Formation of Bound Charges
- Distinction between bound charges and free charges
- Mechanisms of bound charge formation in dielectric materials
- Role of electric dipoles in bound charge distribution
- Properties of Bound Charges
- Localization and inability to move freely
- Interaction with external electric fields
- Creation of an internal electric field within dielectrics
- Significance of Bound Charges
- Influence on the behavior of capacitors
- Enhancement of dielectric properties and energy storage
- Impact on the electric field distribution and potential difference
- Experimental Techniques and Observations
- Measurement methods for characterizing bound charges
- Observations of bound charge behavior in dielectric materials
- Experimental demonstrations of the impact of bound charges
- Theoretical Models and Mathematical Formulations
- Mathematical description of bound charges in dielectrics
- Relationship between polarization, bound charges, and electric fields
- Incorporating bound charges in capacitance calculations and field analysis
- Applications and Future Perspectives
- Practical applications of bound charges in various technologies
- Advances in understanding and manipulating bound charges
- Potential future research directions and challenges
- Conclusion
- Summary of key findings and insights
- Importance of bound charges in the field of electromagnetism
- Significance for technological advancements and future research
This white paper serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding bound charges, offering valuable insights into their formation, properties, significance, experimental observations, theoretical models, and potential applications. By delving into the intricate nature of bound charges, researchers and practitioners can gain a deeper understanding of the behavior of dielectric materials and their impact on electrical systems, ultimately leading to advancements in various fields of science and technology.
