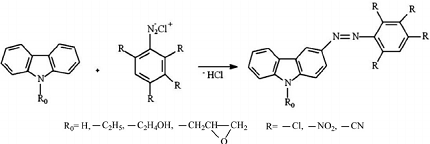
Azo coupling reaction is a type of organic reaction that involves the reaction of a diazonium salt of an aromatic amine with another aromatic compound that contains an electron-rich group, such as an -OH or -NH2 group. The reaction results in the formation of an azo compound, which contains a -N=N- group.
The general reaction mechanism involves the formation of a diazonium salt from the aromatic amine by reaction with nitrous acid (HNO2). The diazonium salt is then reacted with the electron-rich aromatic compound, which acts as a nucleophile and attacks the diazonium cation. The N=N bond is then broken, and the two aromatic rings are joined by the -N=N- group, forming the azo compound.
The reaction is commonly carried out in acidic conditions and at low temperatures, typically around 0-5°C. This is to prevent the diazonium salt from decomposing and to ensure that the reaction proceeds smoothly. A coupling agent, such as copper powder or sodium nitrite, is often added to the reaction mixture to aid in the coupling process.
Azo coupling reactions have a wide range of applications in organic synthesis, including the synthesis of dyes, pigments, and pharmaceuticals.
What is Required Azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines
The azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines requires the following:
- Aromatic amine: The starting material for the reaction is an aromatic amine. The amine must contain an amino group (-NH2) attached to an aromatic ring. The aromatic ring can be substituted with various functional groups, which can affect the reactivity and selectivity of the reaction.
- Nitrous acid: The diazonium salt is generated from the aromatic amine by reaction with nitrous acid (HNO2). Nitrous acid is typically prepared in situ by reacting sodium nitrite (NaNO2) with hydrochloric acid (HCl) or another strong acid.
- Coupling partner: The coupling partner is an electron-rich aromatic compound that contains a functional group capable of reacting with the diazonium cation. Common coupling partners include phenols, anilines, and naphthols.
- Acidic conditions: The reaction is typically carried out in acidic conditions to protonate the amine group and to prevent decomposition of the diazonium salt. Common acids used include hydrochloric acid (HCl) or sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
- Low temperature: The reaction is often carried out at low temperatures, typically around 0-5°C. This is to prevent decomposition of the diazonium salt, which can occur at higher temperatures.
- Coupling agent: A coupling agent, such as copper powder or sodium nitrite, is often added to the reaction mixture to aid in the coupling process.
Overall, the azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines requires careful control of reaction conditions to ensure high yield and selectivity of the desired product.
When is Required Azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines
The azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines is typically used for the synthesis of azo dyes, which are important industrial and commercial compounds used as colorants in textiles, plastics, paints, and other materials. Azo dyes are characterized by their bright and vivid colors, high stability, and ease of synthesis.
The reaction is also used in the synthesis of various aromatic compounds, such as pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. For example, the reaction can be used to synthesize aminophenazone, an analgesic and antipyretic drug used to relieve pain and reduce fever.
Additionally, the azo coupling reaction can be used for the modification of polymers and other materials, to introduce new functional groups and improve their properties. The reaction can also be used for analytical purposes, to detect and quantify the presence of aromatic amines and other compounds in various samples.
Overall, the azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines is a versatile and important tool in organic synthesis, with numerous applications in industry, research, and academia.
Where is Required Azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines
The azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines can be carried out in a laboratory or industrial setting, depending on the desired scale of the reaction. In the laboratory, the reaction is typically carried out on a small scale, using small quantities of reagents and glassware. In an industrial setting, the reaction can be scaled up to produce larger quantities of product, using specialized equipment and facilities.
The reaction is commonly used in the production of azo dyes for the textile, food, and cosmetic industries. The dyeing process involves the use of large quantities of dye, which are produced by the azo coupling reaction on an industrial scale. The reaction is also used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals, which are produced by chemical companies.
Overall, the azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines is a widely used reaction in various industries and research fields, and can be carried out in both laboratory and industrial settings.
How is Required Azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines
The azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines can be carried out using the following general procedure:
- Preparation of the diazonium salt: The starting material, an aromatic amine, is reacted with nitrous acid (HNO2) to form the diazonium salt.
- Preparation of the coupling partner: The coupling partner, an electron-rich aromatic compound, is prepared separately and added to the reaction mixture.
- Mixing the reagents: The diazonium salt solution is added to the coupling partner solution under acidic conditions, and the reaction mixture is stirred.
- Addition of a coupling agent: A coupling agent, such as copper powder or sodium nitrite, is added to the reaction mixture to aid in the coupling process.
- Monitoring the reaction: The progress of the reaction is monitored by TLC (thin layer chromatography) or other analytical techniques.
- Workup: The reaction mixture is quenched with water or dilute acid, and the product is isolated by filtration or extraction.
The reaction conditions can be varied depending on the specific reagents and desired product. For example, the reaction temperature, pH, and choice of coupling partner can affect the yield and selectivity of the reaction. Additionally, various modifications and improvements have been developed to optimize the reaction, such as the use of microwave irradiation or other forms of energy input.
Overall, the azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines is a well-established and versatile reaction, with a wide range of applications in organic synthesis and industry.
Structures of Azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines
The azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines involves the reaction between a diazonium salt and an electron-rich aromatic compound to form an azo compound. The reaction proceeds through the following mechanism:
- Diazotization: The amine reacts with nitrous acid (HNO2) to form the diazonium salt:Ar-NH2 + HNO2 → Ar-N2+ + H2O
- Coupling: The diazonium salt reacts with the electron-rich aromatic compound (coupling partner) under acidic conditions to form the azo compound:Ar-N2+ + Ar’ → Ar-N=N-Ar’ + H+
The resulting azo compound contains a -N=N- functional group, which imparts a characteristic color to the compound. The exact structure of the azo compound depends on the specific reagents used in the reaction.
For example, the coupling of diazonium salt of aniline (C6H5-N2+) with phenol (C6H5OH) produces azobenzene (C6H5-N=N-C6H5):
C6H5-N2+ + C6H5OH → C6H5-N=N-C6H5 + H2O
Similarly, the coupling of diazonium salt of sulfanilic acid (C6H4NH2SO3H-N2+) with naphthol (C10H7OH) produces an orange-red azo dye:
C6H4NH2SO3H-N2+ + C10H7OH → C10H6N2O5S + H2O
Overall, the azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines produces a wide range of azo compounds, with varying colors and properties, making it a versatile reaction with numerous applications.
Case Study on Azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines
One example of the use of the azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines is in the synthesis of azo dyes, which are widely used in the textile industry for dyeing fabrics. A case study involving the synthesis of an azo dye is described below:
Case Study: Synthesis of an Azo Dye
Background: Azo dyes are a class of organic compounds containing the -N=N- functional group, which imparts a characteristic color to the compound. The azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines with electron-rich aromatic compounds is a well-established method for the synthesis of azo dyes.
Procedure:
- Diazotization: Aniline (C6H5NH2) is diazotized with nitrous acid to form the diazonium salt:C6H5NH2 + HNO2 → C6H5N2+ + 2H2O
- Coupling: The diazonium salt is coupled with an electron-rich aromatic compound, such as naphthol (C10H7OH), under acidic conditions to form the azo dye:C6H5N2+ + C10H7OH → C16H12N2O + H2O
- Purification: The crude product is purified by filtration and recrystallization to obtain the final product.
Results:
The synthesis of an azo dye from aniline and naphthol was successful, with the formation of a yellow-orange crystalline compound. The purity of the product was confirmed by melting point determination and spectroscopic analysis (such as UV-vis spectroscopy). The azo dye was then used to dye cotton fabric, resulting in a bright yellow color.
Conclusion:
The azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines is a versatile and widely used method for the synthesis of azo dyes, which are important compounds in the textile industry. The reaction can be optimized by varying the reagents and reaction conditions to achieve the desired product. The resulting azo dyes can be characterized by various analytical techniques, and their properties can be tailored for specific applications.
White paper on Azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines
Introduction:
The azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines is a widely used method for the synthesis of azo compounds, which are important in various fields such as dye chemistry, pharmaceuticals, and materials science. This white paper will provide an overview of the reaction mechanism, applications, and recent advancements in the field.
Reaction Mechanism:
The azo coupling reaction involves the reaction between a diazonium salt (Ar-N2+) and an electron-rich aromatic compound (Ar’) under acidic conditions. The reaction proceeds through the following steps:
- Diazotization: The amine (Ar-NH2) reacts with nitrous acid (HNO2) to form the diazonium salt (Ar-N2+):Ar-NH2 + HNO2 → Ar-N2+ + H2O
- Coupling: The diazonium salt reacts with the electron-rich aromatic compound (Ar’) to form the azo compound (Ar-N=N-Ar’):Ar-N2+ + Ar’ → Ar-N=N-Ar’ + H+
The resulting azo compound contains a -N=N- functional group, which imparts a characteristic color to the compound. The exact structure of the azo compound depends on the specific reagents used in the reaction.
Applications:
The azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines is used in various applications, including:
- Dye synthesis: Azo dyes are synthesized using the azo coupling reaction, and are widely used in the textile industry for dyeing fabrics. The reaction can be optimized by varying the reagents and reaction conditions to achieve the desired product.
- Pharmaceutical synthesis: Azo compounds have been used as drugs for various applications, such as anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents. The azo coupling reaction can be used to synthesize these compounds.
- Materials science: Azo compounds have been used in the synthesis of materials such as polymers, liquid crystals, and sensors. The azo coupling reaction can be used to functionalize these materials with azo groups.
Recent Advancements:
Recent advancements in the field of azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines include:
- Green chemistry: The use of alternative solvents, such as water or ionic liquids, has been explored to make the reaction more environmentally friendly.
- Catalysts: Various catalysts, such as copper and palladium, have been used to enhance the reaction rate and selectivity.
- Mechanistic studies: The reaction mechanism has been studied in detail using spectroscopic and computational methods, leading to a better understanding of the reaction pathway and factors affecting the reaction.
Conclusion:
The azo coupling reaction of diazonium salts of aromatic amines is a versatile and widely used method for the synthesis of azo compounds, with applications in various fields such as dye chemistry, pharmaceuticals, and materials science. Recent advancements in the field have focused on making the reaction more environmentally friendly, enhancing the reaction rate and selectivity, and studying the reaction mechanism in detail.
