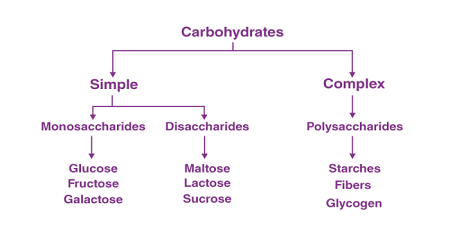
Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients that provide energy to the body. They are organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, with a general formula of (CH2O)n, where “n” can be any number. Carbohydrates are classified based on the number of sugar units they contain:
- Monosaccharides: These are the simplest carbohydrates and cannot be broken down further into simpler sugars. They are composed of a single sugar unit and include glucose, fructose, and galactose.
- Disaccharides: These are composed of two monosaccharides joined together by a glycosidic bond. Examples of disaccharides include sucrose (table sugar), lactose (found in milk), and maltose (found in beer).
- Oligosaccharides: These are composed of 3-10 monosaccharide units joined together by glycosidic bonds. Examples include raffinose and stachyose, found in beans, and fructo-oligosaccharides, found in onions and garlic.
- Polysaccharides: These are composed of many monosaccharide units joined together by glycosidic bonds. Examples include starch (found in plants), glycogen (stored in animals), and cellulose (found in plant cell walls).
Carbohydrates can also be classified as either simple or complex based on their chemical structure and how quickly they are digested and absorbed by the body. Simple carbohydrates are made up of one or two sugar units and are quickly digested and absorbed, leading to a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, are made up of long chains of sugar units and take longer to digest and absorb, resulting in a more gradual increase in blood sugar levels.
What is Required Carbohydrates: Classification
“Required Carbohydrates.” However, as mentioned in my previous response, carbohydrates are classified based on the number of sugar units they contain. The classification of carbohydrates is important because it determines how quickly they are digested and absorbed by the body, as well as their impact on blood sugar levels.
In terms of dietary requirements, carbohydrates are an essential macronutrient that provides the body with energy. The recommended daily intake of carbohydrates varies depending on age, sex, activity level, and overall health. The World Health Organization recommends that carbohydrates should make up between 55-75% of total daily energy intake.
It is also important to note that not all carbohydrates are created equal. Foods that are high in refined carbohydrates, such as sugary drinks and processed snacks, can contribute to weight gain, high blood sugar levels, and other health problems. On the other hand, complex carbohydrates found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables provide essential nutrients and fiber and can help promote a healthy weight and overall health.
When is Required Carbohydrates: Classification
Carbohydrates are required by the body at all times to provide energy for various biological processes. Carbohydrates are an essential macronutrient and are required for proper brain function, muscle function, and other bodily processes.
The classification of carbohydrates is important because it determines how quickly they are digested and absorbed by the body, as well as their impact on blood sugar levels. For example, simple carbohydrates, such as those found in sugar-sweetened beverages and processed snacks, can quickly raise blood sugar levels, while complex carbohydrates, such as those found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, are digested more slowly and have a more gradual effect on blood sugar levels.
The recommended daily intake of carbohydrates varies depending on age, sex, activity level, and overall health. The World Health Organization recommends that carbohydrates should make up between 55-75% of total daily energy intake. However, the quality of the carbohydrates consumed is also important, and it is recommended to focus on consuming carbohydrates from whole food sources rather than processed foods or added sugars.
Where is Required Carbohydrates: Classification
Carbohydrates are found in a variety of foods, including grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. The classification of carbohydrates is based on the number of sugar units they contain and their chemical structure, which can impact how quickly they are digested and absorbed by the body.
Examples of foods that contain simple carbohydrates include sugar-sweetened beverages, candy, and baked goods made with refined flour. These foods are typically high in added sugars and are not considered to be healthy sources of carbohydrates.
Complex carbohydrates are found in foods such as whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables. These foods are rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients, and are considered to be healthy sources of carbohydrates. Whole grain foods include brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole grain bread. Legumes such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas are also good sources of complex carbohydrates.
Fruits and vegetables are also important sources of carbohydrates and contain a variety of vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients. Some examples of high-carbohydrate fruits include bananas, apples, and oranges, while high-carbohydrate vegetables include sweet potatoes, corn, and peas.
It is important to consume a balanced diet that includes a variety of carbohydrate sources to ensure adequate nutrient intake and to support overall health.
How is Required Carbohydrates: Classification
Carbohydrates are classified based on their chemical structure and the number of sugar units they contain. The three main types of carbohydrates are monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates and are made up of a single sugar unit. The most common monosaccharides are glucose, fructose, and galactose.
Disaccharides are made up of two sugar units and include sucrose, which is made up of glucose and fructose, lactose, which is made up of glucose and galactose, and maltose, which is made up of two glucose molecules.
Polysaccharides are made up of many sugar units and can be further classified as either complex or simple carbohydrates. Complex carbohydrates, also known as starches, are made up of many sugar units linked together and are found in foods such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables. Simple carbohydrates, also known as sugars, are made up of shorter chains of sugar units and include foods such as candy, soda, and other sugary treats.
The classification of carbohydrates is important because it can impact how quickly they are digested and absorbed by the body, as well as their impact on blood sugar levels. It is recommended to focus on consuming complex carbohydrates from whole food sources such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, as these provide important nutrients and fiber and have a more gradual impact on blood sugar levels compared to simple carbohydrates found in processed foods and added sugars.
Structures of Carbohydrates: Classification
Carbohydrates are classified based on their chemical structure and the number of sugar units they contain. The three main types of carbohydrates are monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates and are made up of a single sugar unit. The most common monosaccharides are glucose, fructose, and galactose. These monosaccharides have the same chemical formula, C6H12O6, but different structures and properties.
Disaccharides are made up of two sugar units and include sucrose, which is made up of glucose and fructose, lactose, which is made up of glucose and galactose, and maltose, which is made up of two glucose molecules.
Polysaccharides are made up of many sugar units and can be further classified as either complex or simple carbohydrates. Complex carbohydrates, also known as starches, are made up of many sugar units linked together and are found in foods such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables. Simple carbohydrates, also known as sugars, are made up of shorter chains of sugar units and include foods such as candy, soda, and other sugary treats.
Carbohydrates are typically classified based on their molecular structure, which includes the number and arrangement of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. For example, glucose and fructose are both monosaccharides with the same molecular formula (C6H12O6), but their structures differ in the arrangement of their carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
The structure of carbohydrates is important because it determines their function and properties. For example, the branched structure of glycogen, a polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle, allows for rapid breakdown and release of glucose for energy production. The chemical structure of carbohydrates also plays a role in their digestion and absorption in the body, with complex carbohydrates being digested more slowly than simple carbohydrates.
Case Study on Carbohydrates: Classification
Case Study:
Anna is a 35-year-old woman who is looking to improve her diet and overall health. She has read about the importance of carbohydrates in a healthy diet but is confused about the different types of carbohydrates and their classification.
Solution:
Carbohydrates are an important nutrient that provide energy and other essential nutrients to the body. However, not all carbohydrates are created equal. They are classified based on their chemical structure and the number of sugar units they contain.
Monosaccharides, such as glucose, fructose, and galactose, are the simplest form of carbohydrates and are made up of a single sugar unit. Disaccharides, such as sucrose, lactose, and maltose, are made up of two sugar units. Polysaccharides, which include complex carbohydrates and simple carbohydrates, are made up of many sugar units.
Complex carbohydrates, also known as starches, are found in foods such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables. They are made up of many sugar units linked together and are digested more slowly than simple carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates, also known as sugars, are made up of shorter chains of sugar units and include foods such as candy, soda, and other sugary treats.
To improve her diet and overall health, Anna should focus on consuming complex carbohydrates from whole food sources such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. These provide important nutrients and fiber and have a more gradual impact on blood sugar levels compared to simple carbohydrates found in processed foods and added sugars.
It is also important to note that carbohydrates should be consumed in moderation and balanced with other macronutrients such as protein and fat. A balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense whole foods is essential for optimal health.
In summary, understanding the classification of carbohydrates can help individuals make informed choices about their diet and improve their overall health.
White paper on Carbohydrates: Classification
White Paper: Carbohydrates – Classification, Structure and Importance in the Diet
Introduction:
Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients essential for human health, along with protein and fat. They are the main source of energy for the body and are found in a wide range of foods, including grains, fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. In this white paper, we will discuss the classification, structure, and importance of carbohydrates in the diet.
Classification of Carbohydrates:
Carbohydrates can be classified based on their chemical structure and the number of sugar units they contain. The three main types of carbohydrates are monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates and are made up of a single sugar unit. Examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Disaccharides are made up of two sugar units and include sucrose, lactose, and maltose. Polysaccharides are made up of many sugar units and can be further classified as either complex or simple carbohydrates.
Complex carbohydrates, also known as starches, are made up of many sugar units linked together and are found in foods such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables. Simple carbohydrates, also known as sugars, are made up of shorter chains of sugar units and include foods such as candy, soda, and other sugary treats.
Structure of Carbohydrates:
The structure of carbohydrates is important because it determines their function and properties. Carbohydrates are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen atoms is typically 2:1, similar to water. The chemical structure of carbohydrates determines how they are digested and absorbed in the body.
Monosaccharides have a linear or ring structure, depending on the position of the carbonyl group. The ring structure of monosaccharides is important for their function and properties. Disaccharides are formed by the bonding of two monosaccharides through a glycosidic bond. Polysaccharides, such as starch and glycogen, are made up of many sugar units linked together.
Importance of Carbohydrates in the Diet:
Carbohydrates are an essential nutrient for the body and provide energy for physical activity, brain function, and other essential bodily processes. Carbohydrates also play a role in the regulation of blood sugar levels and are an important source of fiber, which helps to support digestive health and promote feelings of fullness.
The type and amount of carbohydrates consumed in the diet can have an impact on overall health. Complex carbohydrates from whole food sources, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, provide important nutrients and fiber and have a more gradual impact on blood sugar levels compared to simple carbohydrates found in processed foods and added sugars. Consuming too many simple carbohydrates and added sugars can lead to negative health consequences, such as weight gain, inflammation, and increased risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Conclusion:
In summary, carbohydrates are an important nutrient in the diet and are classified based on their chemical structure and the number of sugar units they contain. Understanding the classification and structure of carbohydrates can help individuals make informed choices about their diet and improve their overall health. A balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense whole foods, including complex carbohydrates, is essential for optimal health.
