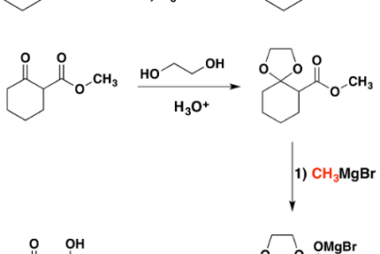
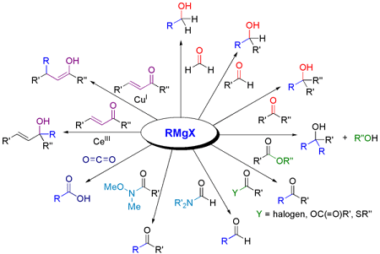
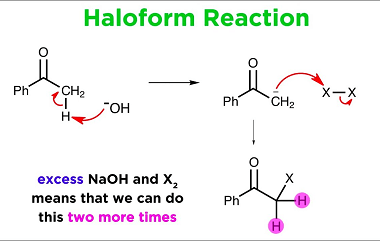
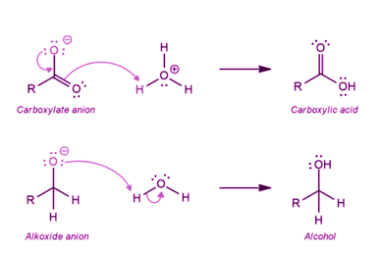
Amine
Amine (pronounced ah-meen) is a given name that is derived from Arabic origins. It is a common name throughout the Arab world and is also used in other cultures. The name means “faithful” or “trustworthy” in Arabic and is often associated with positive qualities such as honesty and reliability. It is a unisex name, meaning…