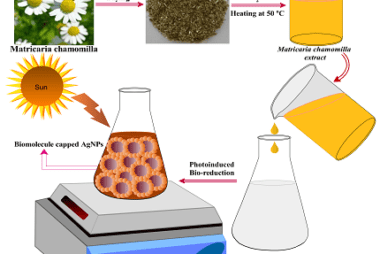
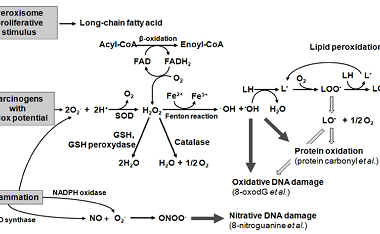
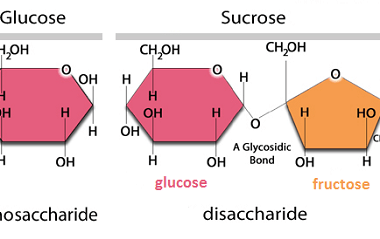
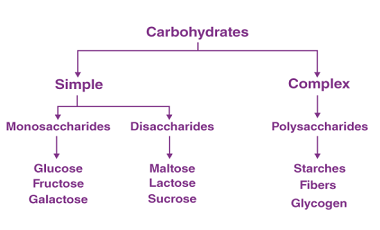
Reduction
Reduction is a chemical reaction that involves the gain of electrons, which results in a decrease in the oxidation state of an atom or molecule. Biomolecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins can undergo reduction reactions. Carbohydrates can undergo reduction to form sugar alcohols, which have important industrial applications. For example, glucose can be reduced…