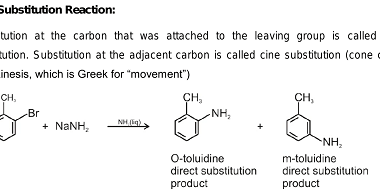
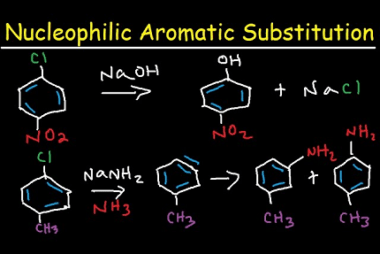
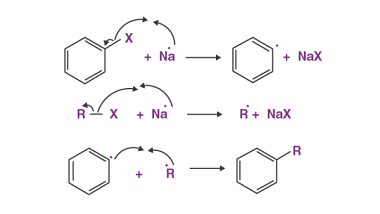
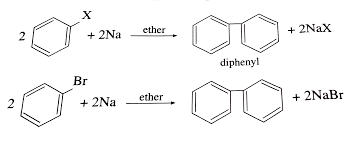
Cine substitution
Haloarenes, which are organic compounds containing at least one halogen atom (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine) attached to an aromatic ring, can undergo cine substitution reactions. Cine substitution reactions involve the substitution of a halogen atom on a benzene ring by a nucleophile, such as an amine, hydroxide ion, or cyanide ion, at the ortho…