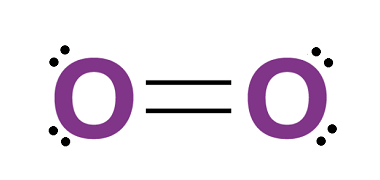
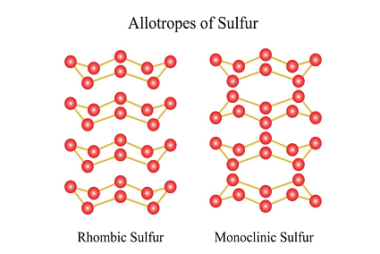
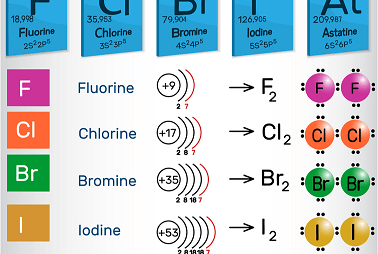
Group 16 Oxoacids of sulfur
Sulfur forms a variety of oxoacids, which are acids that contain oxygen and sulfur. There are several oxoacids of sulfur, but the most common ones are the Group 16 oxoacids of sulfur, which include sulfuric acid, sulfurous acid, thiosulfuric acid, and dithionic acid. All of these oxoacids of sulfur have important industrial and commercial applications,…