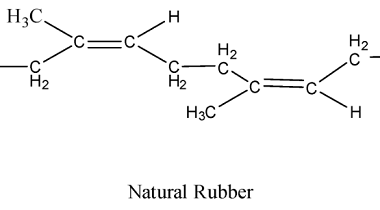
Applications of polymers
Polymers are a diverse group of materials with many applications in various industries. Some of the common applications of polymers are: Overall, polymers have a wide range of applications in many industries, making them a crucial material in the modern world. What is Required Applications of polymers The required applications of polymers depend on the…