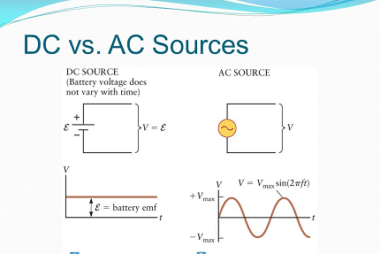
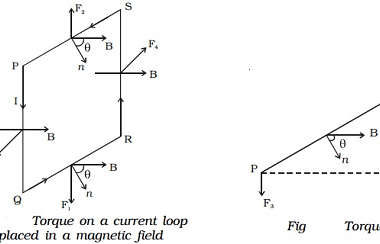
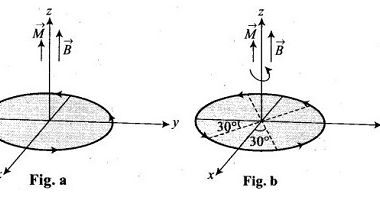
With d.c. and a.c. sources
DC (direct current) and AC (alternating current) are two types of electrical power sources. DC sources provide a steady and constant flow of electrical energy in one direction. Batteries, fuel cells, and photovoltaic cells are common examples of DC sources. AC sources, on the other hand, provide electrical energy that alternates in direction and magnitude…