On a current-carrying wire in a uniform magnetic field
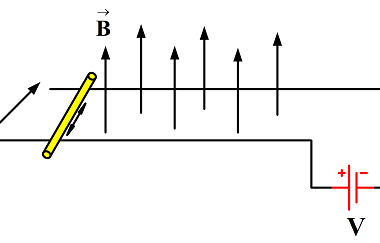
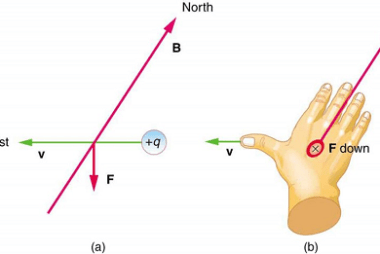
When a current-carrying wire is placed in a uniform magnetic field, a magnetic force is exerted on the wire. This force is perpendicular to both the direction of the current in the wire and the direction of the magnetic field. The magnitude of the force is given by the equation F = BIL, where F…