Uniformly charged thin spherical shell
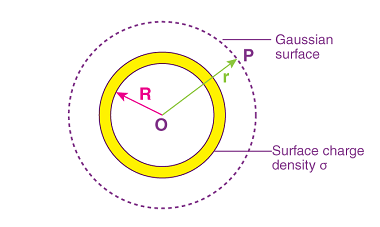
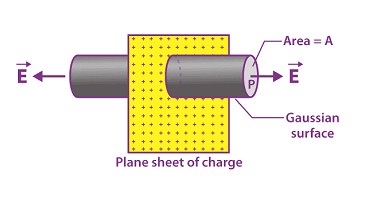
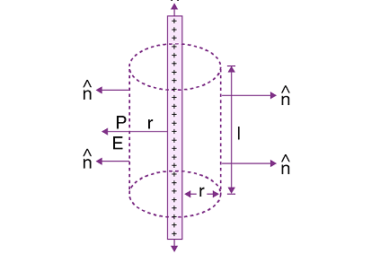
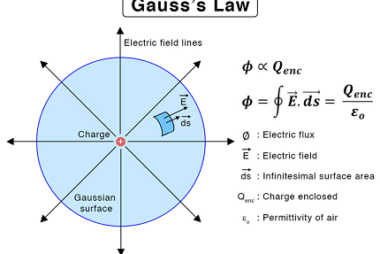
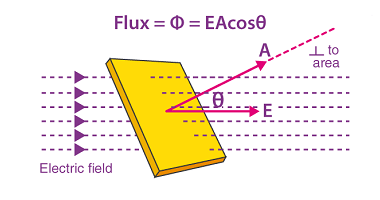
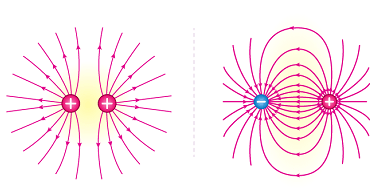
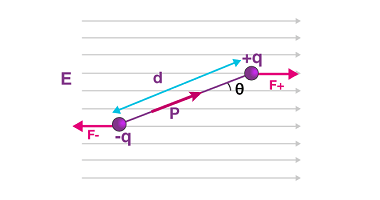
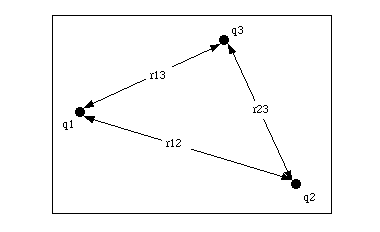
A uniformly charged thin spherical shell refers to a hollow spherical shell with a uniform charge density. The charge density is the amount of charge per unit volume of the shell. This type of system is often studied in electrostatics and can be analyzed using Gauss’s law, which relates the electric flux through a closed…