Doppler effect (in sound)
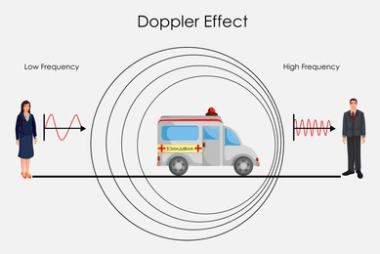
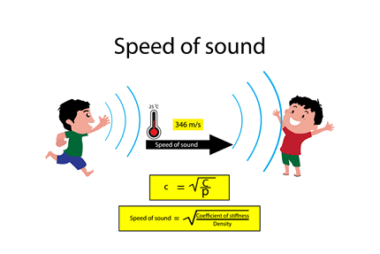
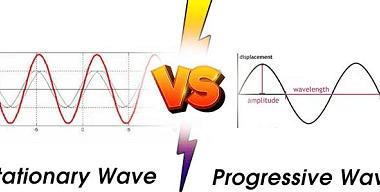
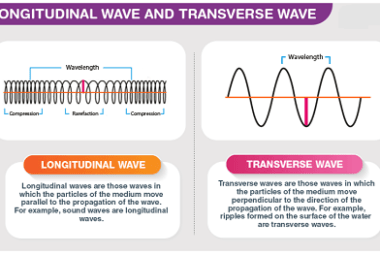
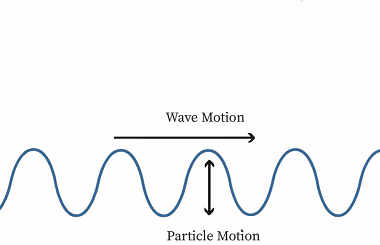
The Doppler effect is the change in frequency or wavelength of a sound wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the source of the sound. This effect is named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who first described the phenomenon in 1842. When a sound source is moving towards an observer,…