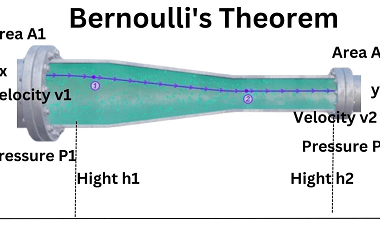
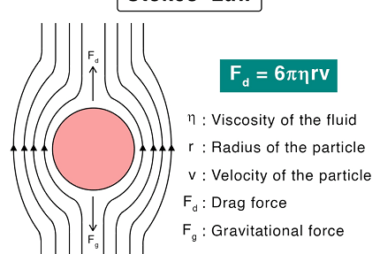
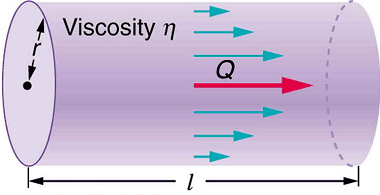
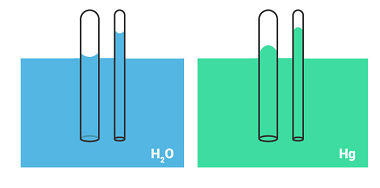
Bernoulli’s theorem
Bernoulli’s theorem, named after the Swiss mathematician Daniel Bernoulli, is a fundamental principle of fluid dynamics that describes the relationship between the pressure, velocity, and elevation of a fluid in motion. It states that as the speed of a fluid increases, the pressure within the fluid decreases, and vice versa. In mathematical terms, Bernoulli’s theorem…