De Broglie wavelength of matter waves
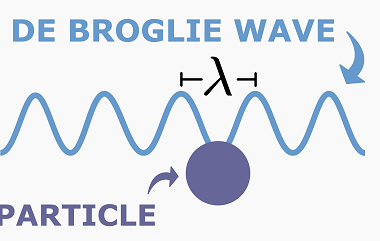
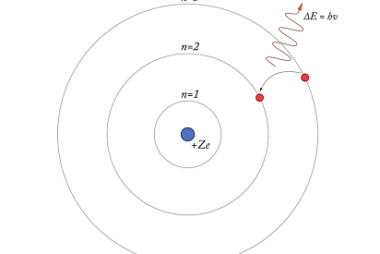
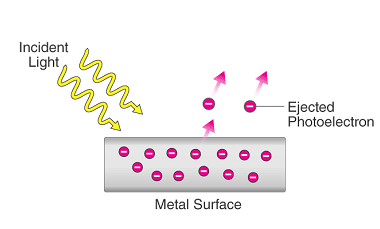
The de Broglie wavelength is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics that describes the wave-like nature of matter particles, such as electrons, protons, and atoms. It is named after Louis de Broglie, who proposed that all matter particles have a wave-like nature in addition to their particle-like nature. The de Broglie wavelength (λ) is given…