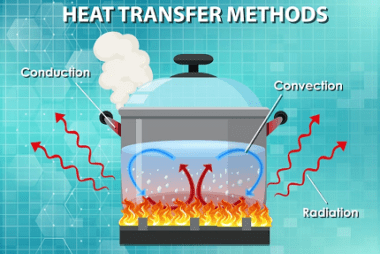
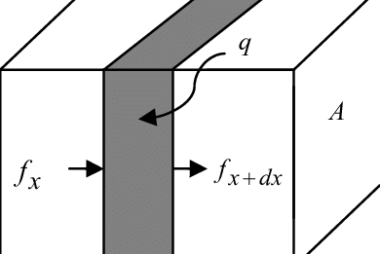
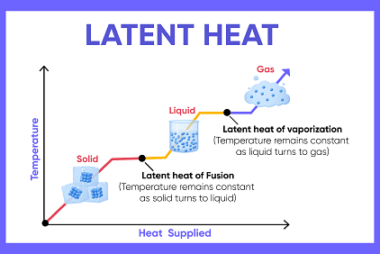
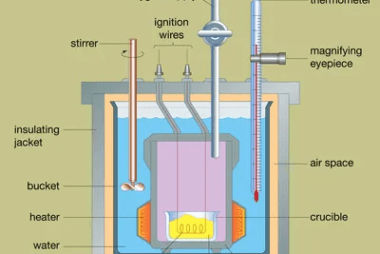
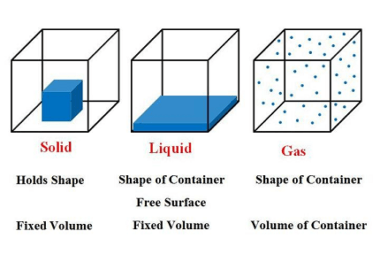
Elementary concepts of convection
Convection is the transfer of heat by the motion of a fluid such as air or water. The basic concepts of convection include: Overall, convection is an important process for heat transfer in many applications, from cooling electronic devices to heating homes and buildings. What is Required Elementary concepts of convection To understand the elementary…