Advance Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Brownian movement
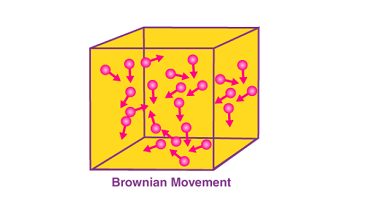
Brownian movement Brownian movement, also known as Brownian motion, is the random motion of microscopic particles suspended in a fluid (liquid or gas). It was first observed by the botanist Robert Brown in 1827 and later explained by Albert Einstein in 1905. Brownian movement occurs due to the continuous collision of the fluid molecules with…