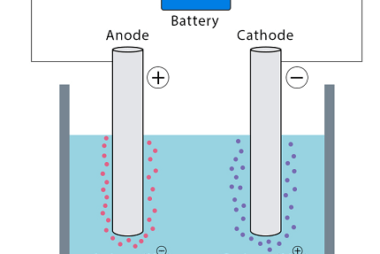
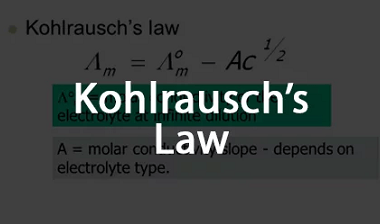
Advance Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Temperature
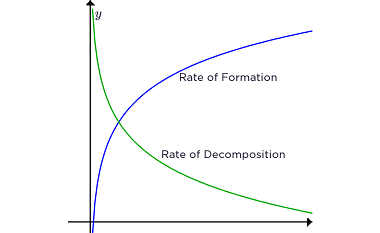
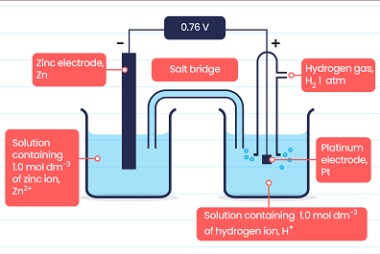
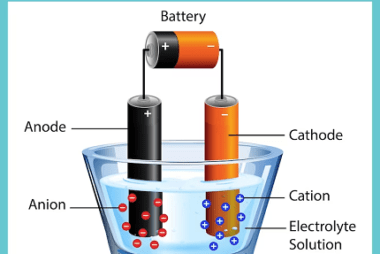
Temperature Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance or system. It represents the degree of hotness or coldness of an object or environment. In scientific terms, temperature is often measured in degrees Celsius (°C), Fahrenheit (°F), or Kelvin (K). Here are some key points about temperature: Understanding…