Advance Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Redox reaction
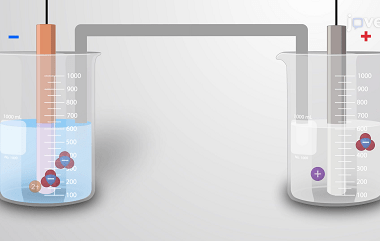
Redox reaction A redox reaction, short for reduction-oxidation reaction, is a chemical reaction in which there is a transfer of electrons between species. In a redox reaction, one substance undergoes oxidation (loses electrons) while another substance undergoes reduction (gains electrons). The key components of a redox reaction are: Redox reactions are commonly encountered in various…