Crash Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus A system of charges
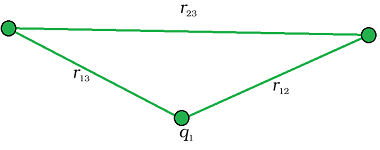
A system of charges In the context of the AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) entrance exam, the physics syllabus covers various topics related to the system of charges. This includes the study of electrostatics and the behavior of charged particles in different systems. Here are some important topics you should focus on: Make…