Advance Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Mutual Inductance
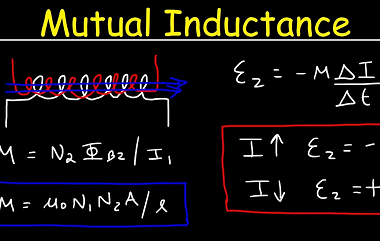
Mutual Inductance Mutual inductance is a phenomenon that occurs when two or more coils of wire are placed close to each other. It describes the ability of one coil to induce an electromotive force (emf) in another coil through the changing magnetic field produced by the current flowing in the first coil. The mutual inductance,…