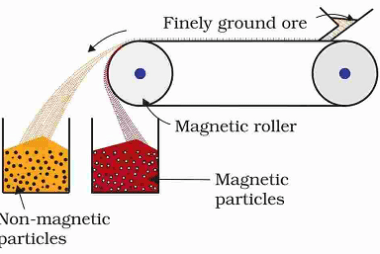
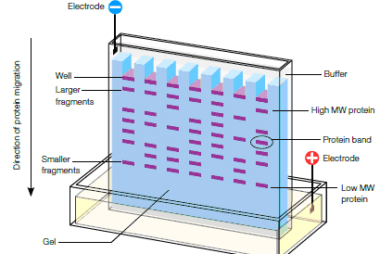
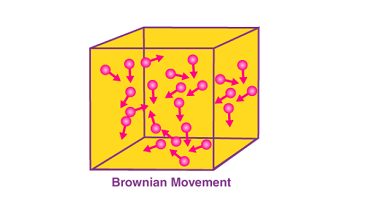
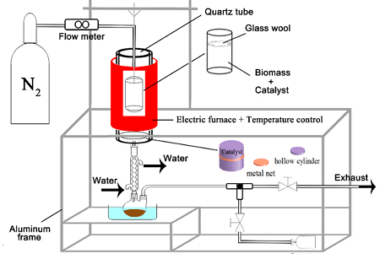
Advance Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Oxidation
Oxidation Oxidation is a chemical process that involves the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state of an atom, ion, or molecule. It is often associated with the addition of oxygen, the removal of hydrogen, or the removal of electrons from a species. Oxidation reactions are typically accompanied by reduction reactions, forming…