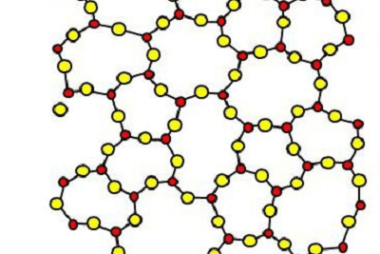
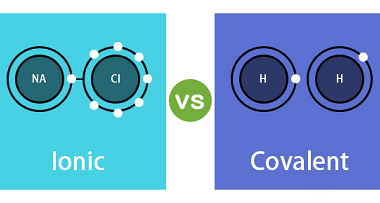
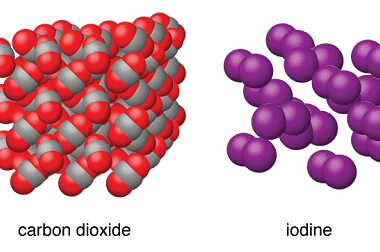
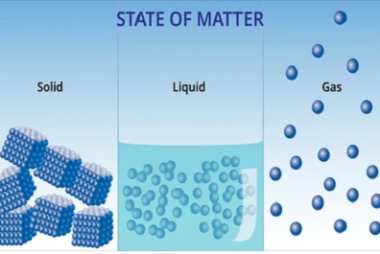
Advance Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus The solubility of the gas in liquids
The solubility of the gas in liquids The solubility of a gas in a liquid refers to the ability of the gas to dissolve in the liquid. It is influenced by factors such as temperature, pressure, and the nature of the gas and liquid involved. When the pressure of the gas above the liquid increases,…