Integrated Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Spherical Mirrors
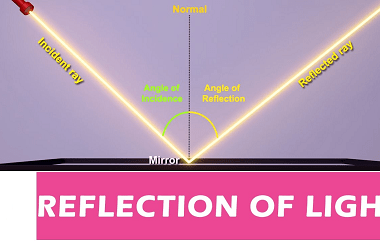
Spherical Mirrors Spherical mirrors are curved mirrors with a spherical shape. They can be either concave or convex, depending on the curvature of the reflecting surface. These mirrors are widely used in various optical devices and systems. Key characteristics and properties of concave mirrors include: Applications of concave mirrors include telescopes, shaving mirrors, headlights, and…