Integrated Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Current loop as a magnetic dipole
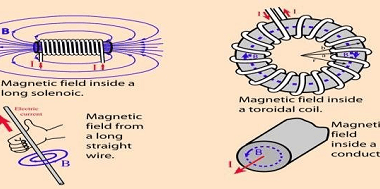
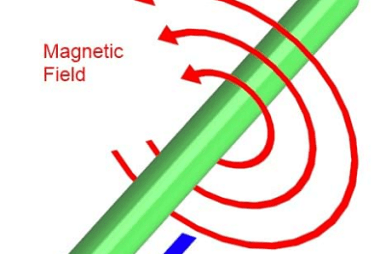
Current loop as a magnetic dipole A current loop can be considered as a magnetic dipole due to its magnetic properties. When electric current flows through a closed loop, it generates a magnetic field around it, similar to a bar magnet. This magnetic field is responsible for the loop’s behavior as a magnetic dipole. Here…