Integrated Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Continuous charge distribution
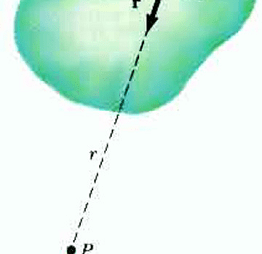
Continuous charge distribution Continuous charge distribution refers to a situation where electric charge is distributed continuously over a region rather than being concentrated at discrete points. In contrast to discrete charge distributions, which involve individual charges at specific locations, continuous charge distributions involve a charge density that varies continuously throughout a given region. Continuous charge…