Integrated Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Solid Solutions
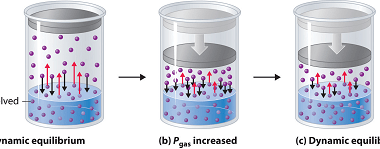
Solid Solutions Solid solutions are homogeneous mixtures of two or more substances in the solid state. They are formed when atoms, ions, or molecules of one substance (solutes) are uniformly dispersed within the crystal lattice of another substance (solvent) at the atomic or molecular level. The solute particles occupy interstitial or substitutional positions within the…