Integrated Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Matter waves
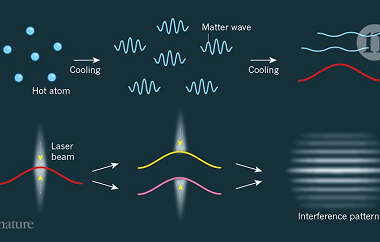
Matter waves Matter waves, also known as de Broglie waves, are a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics that describes the wave-like behavior of particles. According to the wave-particle duality principle, particles, such as electrons, protons, and even larger objects like atoms and molecules, can exhibit wave-like properties. The concept of matter waves originated from Louis…