Integrated Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Carbon Resistors
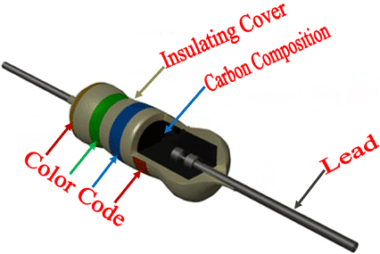
Carbon Resistors Carbon resistors are electronic components commonly used in electrical circuits to provide resistance. They are made of a cylindrical rod of carbon with metal end caps and color-coded bands that indicate their resistance value. Here are some key points about carbon resistors: It’s worth noting that while carbon resistors have been widely used…