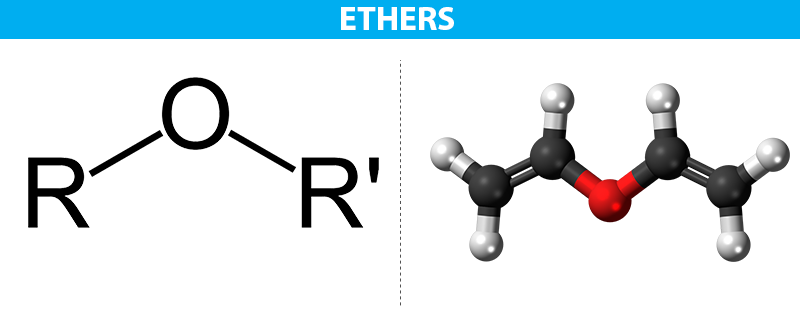
Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula R-O-R’, where R and R’ are alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers are important in organic chemistry because they are widely used as solvents and as intermediates in the synthesis of other organic compounds.
Some of the important topics related to ethers in the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course include:
- Nomenclature of Ethers: The IUPAC rules for naming ethers involve identifying the two alkyl or aryl groups attached to the oxygen atom and combining their names with the word “ether”. The naming conventions for cyclic ethers are slightly different.
- Physical Properties of Ethers: Ethers are generally less polar than alcohols but more polar than hydrocarbons. They have lower boiling points than alcohols of similar molecular weight but higher boiling points than hydrocarbons of similar molecular weight.
- Preparation of Ethers: Ethers can be prepared by the Williamson ether synthesis, which involves the reaction of an alkoxide ion with a primary alkyl halide or tosylate. Ethers can also be prepared by the acid-catalyzed dehydration of alcohols.
- Reactions of Ethers: Ethers are relatively unreactive but can undergo acid-catalyzed cleavage to form alcohols and alkyl halides. They can also be oxidized to form peroxides, which can be explosive.
- Crown Ethers: Crown ethers are cyclic ethers that contain several oxygen atoms. They are important in coordination chemistry because they can selectively bind to metal ions and other guest molecules.
- Ethers as Solvents: Ethers are widely used as solvents in organic chemistry because they are relatively inert and have low toxicity. Some common ethers used as solvents include diethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran (THF), and dioxane.
These are some of the key topics related to ethers that are covered in the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course. It is important for students to have a strong understanding of these topics in order to succeed in organic chemistry.
History of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Ethers
The study of ethers has a long history in organic chemistry, dating back to the mid-19th century. In 1851, German chemist August Wilhelm von Hofmann first synthesized diethyl ether by heating ethanol with sulfuric acid. This discovery paved the way for further research into the properties and reactions of ethers.
Over the years, researchers discovered new methods for preparing ethers, including the Williamson ether synthesis, which was developed by Alexander Williamson in 1851. This method involves the reaction of an alkoxide ion with a primary alkyl halide or tosylate to form an ether.
In the late 19th century, researchers also began to explore the use of ethers as anesthetics. In 1846, American dentist William Morton first used ether as an anesthetic during a dental procedure, and this discovery revolutionized the field of medicine.
During the early 20th century, researchers continued to study the properties and reactions of ethers, and new methods for preparing cyclic ethers were developed. In 1967, Charles Pedersen discovered crown ethers, a type of cyclic ether that can selectively bind to metal ions and other guest molecules. This discovery led to the development of new applications for ethers in coordination chemistry and molecular recognition.
In modern times, the study of ethers remains an important area of research in organic chemistry, with new methods for synthesizing and using ethers being developed all the time. The study of ethers is an important part of the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in organic chemistry, as it provides students with a solid foundation in the principles and applications of this important class of organic compounds.
Nature of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Ethers
The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course on ethers covers a wide range of topics related to the nature, properties, and reactions of ethers. Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups. Some of the key topics covered in the course include:
- Physical properties of ethers: Ethers are generally less polar than alcohols but more polar than hydrocarbons. They have lower boiling points than alcohols of similar molecular weight but higher boiling points than hydrocarbons of similar molecular weight. These properties make ethers useful as solvents in organic chemistry.
- Preparation of ethers: Ethers can be prepared by a variety of methods, including the Williamson ether synthesis, which involves the reaction of an alkoxide ion with a primary alkyl halide or tosylate, and acid-catalyzed dehydration of alcohols.
- Reactions of ethers: Ethers are relatively unreactive but can undergo acid-catalyzed cleavage to form alcohols and alkyl halides. They can also be oxidized to form peroxides, which can be explosive. Crown ethers, a type of cyclic ether, can selectively bind to metal ions and other guest molecules.
- Applications of ethers: Ethers are widely used as solvents in organic chemistry because they are relatively inert and have low toxicity. Some common ethers used as solvents include diethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran (THF), and dioxane. Ethers are also used as anesthetics and as intermediates in the synthesis of other organic compounds.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course on ethers provides students with a comprehensive understanding of the nature and properties of this important class of organic compounds. Students who successfully complete this course will have a strong foundation in the principles and applications of ethers, which will be useful in further study of organic chemistry and in practical applications in industry and medicine.
Importance of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Ethers
The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course on ethers is important for several reasons:
- Foundational knowledge: Ethers are a fundamental class of organic compounds, and the intermediate course provides students with a thorough understanding of their nature, properties, and reactions. This foundational knowledge is essential for further study in organic chemistry.
- Industrial applications: Ethers are widely used as solvents in the chemical industry, particularly in the production of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and specialty chemicals. Knowledge of ethers and their properties is essential for careers in the chemical industry.
- Medical applications: Ethers have important medical applications as anesthetics, and a thorough understanding of their properties and reactions is essential for medical professionals.
- Environmental concerns: Ethers are often used as solvents, and their disposal can have negative impacts on the environment. A thorough understanding of the properties and reactions of ethers is essential for environmentally responsible use and disposal of these compounds.
- Research applications: Ethers have a wide range of applications in chemical research, particularly in the fields of coordination chemistry and molecular recognition. Knowledge of ethers and their properties is essential for researchers working in these areas.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course on ethers is important for providing students with a strong foundation in organic chemistry and preparing them for careers in the chemical industry, medicine, and research.
Benefits of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Ethers
The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course on ethers offers several benefits to students who study this subject. Some of the main benefits include:
- Understanding the fundamental principles of organic chemistry: Ethers are a fundamental class of organic compounds, and studying their properties and reactions helps students to develop a deep understanding of the principles of organic chemistry.
- Preparing for advanced study: Knowledge of ethers is essential for further study in organic chemistry and related fields. Students who complete the intermediate course will be well-prepared for advanced study in these areas.
- Enhancing career prospects: Ethers are widely used in the chemical industry, particularly as solvents in the production of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and specialty chemicals. Knowledge of ethers and their properties is essential for careers in these areas.
- Advancing medical knowledge: Ethers have important medical applications as anesthetics, and a thorough understanding of their properties and reactions is essential for medical professionals.
- Contributing to environmental responsibility: Knowledge of ethers and their properties is essential for environmentally responsible use and disposal of these compounds, helping to reduce the impact of chemical waste on the environment.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course on ethers offers a range of benefits to students, including a strong foundation in organic chemistry, preparation for advanced study, enhanced career prospects, contributions to medical knowledge, and environmental responsibility.
Conclusion of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Ethers
In conclusion, the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course on ethers is an essential component of the study of organic chemistry. Ethers are a fundamental class of organic compounds with a wide range of applications in the chemical industry, medicine, research, and environmental responsibility. The course covers the nature, properties, and reactions of ethers, including their physical properties, preparation methods, and applications. Students who successfully complete the course will have a thorough understanding of the principles and applications of ethers, providing them with a strong foundation for further study in organic chemistry and related fields, and enhancing their career prospects in the chemical industry, medicine, and research. Overall, the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course on ethers is an essential component of the study of organic chemistry and has important implications for a range of scientific, medical, and environmental applications.
Overview of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Ethers
The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course on ethers is a comprehensive study of the nature, properties, and reactions of ethers, which are a fundamental class of organic compounds. The course covers the physical properties of ethers, including their boiling point, solubility, and volatility. It also covers the methods for the preparation of ethers, including Williamson synthesis, acid-catalyzed dehydration of alcohols, and others. The course also includes a study of the reactions of ethers, such as acid-catalyzed cleavage, nucleophilic substitution, and other reactions.
The intermediate course on ethers has several important applications, including industrial, medical, research, and environmental applications. Ethers are widely used as solvents in the chemical industry, particularly in the production of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and specialty chemicals. They also have important medical applications as anesthetics, and a thorough understanding of their properties and reactions is essential for medical professionals. Ethers have a wide range of applications in chemical research, particularly in the fields of coordination chemistry and molecular recognition. Knowledge of ethers and their properties is also essential for environmentally responsible use and disposal of these compounds.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course on ethers is an essential component of the study of organic chemistry, providing students with a thorough understanding of the principles and applications of this important class of organic compounds. The course prepares students for advanced study in organic chemistry and related fields and enhances their career prospects in the chemical industry, medicine, and research.
Types of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Ethers
The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course on ethers covers several types of ethers, including:
- Simple Ethers: These are ethers in which both alkyl or aryl groups are the same. Examples include dimethyl ether, diethyl ether, and dibutyl ether.
- Mixed Ethers: These are ethers in which the two alkyl or aryl groups are different. Examples include methyl ethyl ether, ethyl propyl ether, and phenyl ethyl ether.
- Cyclic Ethers: These are ethers in which the oxygen atom is a part of a ring structure. Examples include tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, and crown ethers.
- Unsaturated Ethers: These are ethers that contain one or more double bonds. Examples include vinyl ether, allyl ether, and butadiene oxide.
- Heterocyclic Ethers: These are cyclic ethers that contain at least one heteroatom other than oxygen in the ring. Examples include pyran, pyridine oxide, and thiirane.
The intermediate course on ethers covers the physical and chemical properties of these different types of ethers, including their boiling point, solubility, stability, and reactivity. The course also covers the methods for the preparation of these ethers, as well as their reactions and applications in the chemical industry, medicine, and research.
Structures of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Ethers
The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course on ethers covers several structures of ethers, including:
- Simple Ethers: These have the general structure R-O-R’, where R and R’ are alkyl or aryl groups. Examples include ethyl methyl ether (CH3OCH2CH3) and diethyl ether (CH3CH2OCH2CH3).
- Mixed Ethers: These have the general structure R-O-R’, where R and R’ are different alkyl or aryl groups. Examples include ethyl propyl ether (CH3CH2OCH2CH2CH3) and phenyl ethyl ether (C6H5OCH2CH3).
- Cyclic Ethers: These have the general structure R-O-R’, where R and R’ are part of a cyclic structure that includes an oxygen atom. Examples include tetrahydrofuran (THF, C4H8O), dioxane (C4H8O2), and crown ethers such as 18-crown-6 (C12H24O6).
- Unsaturated Ethers: These have the general structure R-O-R’ where R and R’ are alkyl or aryl groups and at least one of the groups is connected to an unsaturated carbon atom. Examples include vinyl ether (C2H3OC2H3) and allyl ether (CH2=CHCH2OC2H5).
- Heterocyclic Ethers: These have the general structure R-O-R’ where R and R’ are part of a cyclic structure that includes a heteroatom other than oxygen, such as nitrogen or sulfur. Examples include pyran (C5H8O), pyridine oxide (C5H5NO), and thiirane (C2H4S).
The intermediate course on ethers covers the properties, reactions, and applications of these different ether structures, including their physical and chemical properties, methods for their synthesis, and their uses in industry, medicine, research, and environmental responsibility.
Application of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Ethers
Ethers are organic compounds that have an oxygen atom between two carbon atoms. They are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Solvent: Ethers are commonly used as solvents in industrial and laboratory settings. Diethyl ether, for example, is a common solvent used in chemical reactions.
- Anesthetic: Diethyl ether was historically used as a general anesthetic, but has largely been replaced by safer alternatives in modern medicine.
- Fuel additive: Methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) has been used as a fuel additive to increase octane ratings in gasoline, although its use has declined due to environmental concerns.
- Flavoring agent: Ethers such as ethyl methyl ether and isopropyl ethyl ether are used as flavoring agents in food products.
- Fragrance: Some ethers, such as ethyl ether and isopropyl ether, have pleasant odors and are used in perfumes and colognes.
In terms of their application in JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate courses, ethers are important compounds to study in organic chemistry. They are commonly used in organic synthesis reactions, and knowledge of their properties and reactivity can be essential in designing new reactions or understanding existing ones. In addition, ethers are frequently tested on JEE exams, so a solid understanding of their properties and reactions is crucial for success on these tests.
Nomenclature of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Ethers
The nomenclature of ethers follows the standard IUPAC rules for naming organic compounds. The name of an ether is derived from the names of the two alkyl or aryl groups bonded to the oxygen atom, with the prefix “ether” added to indicate the functional group. The basic format for naming ethers is:
alkyl/aryl group + oxy + alkyl/aryl group + ether
For example, the ether formed by the reaction of ethyl alcohol and methyl alcohol is named ethyl methyl ether, since the two alkyl groups are ethyl and methyl.
If one of the alkyl or aryl groups is more complex, it is named first, followed by the simpler group. For example, the ether formed by the reaction of benzene and methyl alcohol is named methyl phenyl ether, since the aryl group is benzene and the alkyl group is methyl.
If there are multiple substituents on the same alkyl or aryl group, they are listed in alphabetical order, with the prefix “di-” or “tri-” added to indicate the number of substituents. For example, the ether formed by the reaction of isopropyl alcohol and ethyl alcohol is named isopropyl ethyl ether.
It is important to note that when naming ethers, the two alkyl or aryl groups are separated by the word “oxy,” not a hyphen.
Career Opportunities of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Ethers
As an intermediate course in organic chemistry, the study of ethers in JEE (Main+Advance) can open up a range of career opportunities in various fields. Here are some potential career paths for those with a strong foundation in organic chemistry and experience with ethers:
- Chemical research and development: The pharmaceutical and chemical industries require skilled chemists to conduct research and develop new products. Knowledge of ethers and their properties can be valuable in developing new drugs, solvents, or other chemicals.
- Process development and optimization: Chemical engineers work to optimize chemical processes for maximum efficiency and yield. Understanding the reactivity of ethers and their use as solvents or reactants can be important in designing and improving these processes.
- Quality control and analysis: Chemists and chemical engineers may work in quality control and analysis, ensuring that products meet specific standards and specifications. Understanding the properties and reactivity of ethers can be valuable in this role.
- Regulatory affairs and compliance: Chemical companies must comply with a range of regulations and standards. Those with a strong understanding of chemistry and organic compounds like ethers can work in regulatory affairs to ensure that their company is in compliance with local and national regulations.
- Academia and teaching: Those with a deep understanding of organic chemistry, including ethers, can pursue careers in academia, teaching, and research.
- Environmental science: Ethers, such as MTBE, have been shown to have negative impacts on the environment. Those with an understanding of the properties of ethers and their environmental impact can pursue careers in environmental science and policy.
