Aldehydes and ketones are important organic compounds that are commonly tested in JEE (Main+Advanced) exams. As a repeater, it is important to have a good understanding of these compounds and their properties. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
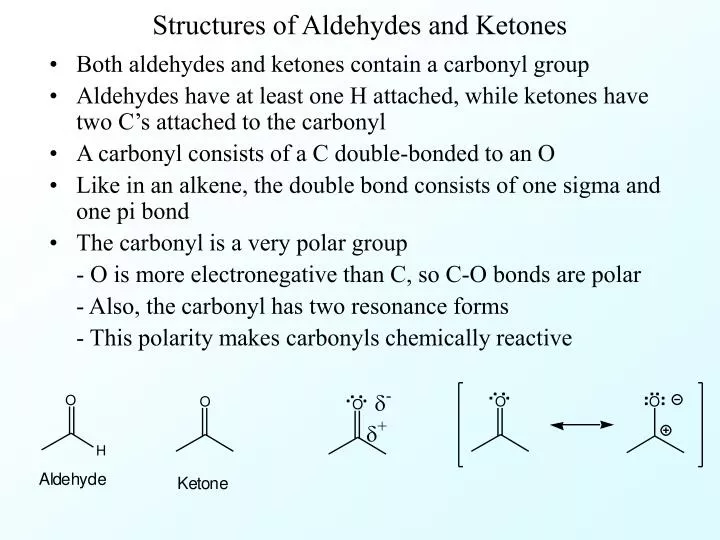
- Aldehydes and ketones are both carbonyl compounds, which means they contain a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom.
- The carbonyl group in aldehydes is located at the end of a carbon chain, whereas in ketones it is located in the middle.
- Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e ending of the corresponding parent alkane with -al, while ketones are named by replacing the -e ending of the corresponding parent alkane with -one.
- Aldehydes can be oxidized to form carboxylic acids, while ketones cannot be oxidized further.
- Both aldehydes and ketones can undergo nucleophilic addition reactions, which involve the attack of a nucleophile (such as a hydroxide ion) on the carbonyl carbon atom.
- Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones towards nucleophiles because the carbonyl carbon in aldehydes is less hindered than in ketones.
- Aldehydes and ketones can also undergo reduction reactions, such as the addition of hydrogen or hydride ions, to form alcohols.
- Aldehydes and ketones can be distinguished by their different reactions with Tollens’ reagent and Fehling’s solution. Aldehydes are oxidized by Tollens’ reagent to form a silver mirror, while ketones do not react. Fehling’s solution, on the other hand, reacts with aldehydes to form a red precipitate of copper(I) oxide, while ketones do not react.
Make sure to review these concepts thoroughly and practice solving JEE (Main+Advanced) problems related to aldehydes and ketones. Good luck!
History of JEE (Main+Advance) Repeater Course Aldehydes and Ketones
The Joint Entrance Examination (JEE) is an engineering entrance exam in India that is conducted for admission into various undergraduate engineering and architecture programs at prestigious institutes like the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), the National Institutes of Technology (NITs), and other government-funded engineering colleges.
The JEE (Main+Advanced) exam was introduced in 2013 as a replacement for the earlier format of the exam, which was known as the Indian Institutes of Technology Joint Entrance Examination (IIT-JEE). The new format consisted of two stages – JEE Main and JEE Advanced.
The syllabus for JEE (Main+Advanced) includes a wide range of topics in mathematics, physics, and chemistry. The study of aldehydes and ketones is an important part of the organic chemistry section of the chemistry syllabus.
The study of aldehydes and ketones has a long and rich history in the field of organic chemistry. Aldehydes were first isolated in the early 19th century by chemists such as Justus von Liebig and Friedrich Wöhler. In 1834, Liebig proposed the term “aldehyde” for the substance that was obtained by the partial oxidation of alcohol.
Ketones were first isolated in the mid-19th century by chemists such as August Kekulé and Charles Frédéric Gerhardt. Kekulé proposed the term “ketone” for the substance that was obtained by the dry distillation of calcium acetate.
Over the years, the study of aldehydes and ketones has continued to evolve, with new methods for their synthesis and reactions being discovered. Today, aldehydes and ketones are important compounds in fields such as pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and flavors and fragrances.
For JEE (Main+Advanced) repeater courses, the study of aldehydes and ketones is an important part of the organic chemistry section of the syllabus. It is essential for students to have a thorough understanding of the properties and reactions of these compounds to succeed in the exam.
Importance of JEE (Main+Advance) Repeater Course Aldehydes and Ketones
The study of aldehydes and ketones is an important part of the JEE (Main+Advanced) repeater course in organic chemistry. Here are some reasons why aldehydes and ketones are important topics to study for the exam:
- They are commonly tested in the JEE (Main+Advanced) exam: Questions related to aldehydes and ketones are frequently asked in the organic chemistry section of the exam. Therefore, it is essential for repeater students to have a good understanding of these compounds and their properties.
- They are important intermediates in organic synthesis: Aldehydes and ketones are versatile intermediates that can be used to synthesize a wide range of organic compounds, including alcohols, acids, and amines. Therefore, a good understanding of aldehydes and ketones is essential for students who want to pursue careers in organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, or materials science.
- They are used in the production of important products: Aldehydes and ketones are used in the production of many important products, including perfumes, flavors, and plastics. Therefore, a good understanding of these compounds is essential for students who want to pursue careers in these industries.
- They illustrate important principles in organic chemistry: The study of aldehydes and ketones helps students to understand important principles in organic chemistry, including nucleophilic addition reactions, oxidation-reduction reactions, and stereochemistry. These principles are important for understanding a wide range of organic reactions and mechanisms.
Overall, the study of aldehydes and ketones is an essential part of the JEE (Main+Advanced) repeater course in organic chemistry. Students who master these concepts will have a solid foundation in organic chemistry and will be well-prepared to succeed on the exam and pursue careers in a variety of fields.
System of JEE (Main+Advance) Repeater Course Aldehydes and Ketones
The JEE (Main+Advanced) repeater course in aldehydes and ketones covers a wide range of topics related to these organic compounds. Here is an overview of the system of the course:
- Introduction: The course typically starts with an introduction to aldehydes and ketones, their general structure, nomenclature, and physical properties.
- Preparation: Students will learn various methods for the preparation of aldehydes and ketones, including oxidation of alcohols, ozonolysis of alkenes, and Friedel-Crafts acylation.
- Properties and reactions: The course covers the properties of aldehydes and ketones, including their acidity, basicity, and reactivity towards nucleophiles and electrophiles. Students will also learn about various reactions of aldehydes and ketones, including nucleophilic addition reactions, oxidation-reduction reactions, and condensation reactions.
- Stereochemistry: The course includes a discussion of the stereochemistry of aldehydes and ketones, including the concept of enantiomers and diastereomers and their optical activity.
- Applications: The course covers the applications of aldehydes and ketones in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, flavors, and fragrances. Students will also learn about the role of aldehydes and ketones in the synthesis of important organic compounds, such as amino acids and carbohydrates.
Throughout the course, students will be expected to solve practice problems and participate in group discussions to reinforce their understanding of the material. The course may also include laboratory experiments to give students hands-on experience with the preparation and reactions of aldehydes and ketones. By the end of the course, students should have a solid understanding of aldehydes and ketones and be well-prepared to tackle related questions on the JEE (Main+Advanced) exam.
Conclusion of JEE (Main+Advance) Repeater Course Aldehydes and Ketones
In conclusion, the JEE (Main+Advanced) repeater course in aldehydes and ketones is an important part of the organic chemistry syllabus. It covers a wide range of topics related to these organic compounds, including their preparation, properties, reactions, stereochemistry, and applications.
Students who master the material covered in the course will be well-prepared to succeed on the JEE (Main+Advanced) exam and pursue careers in various fields related to organic chemistry, including pharmaceuticals, flavors, fragrances, and materials science. In addition to providing a solid foundation in organic chemistry, the course also helps students develop critical thinking skills and problem-solving abilities that will be useful in many different areas of science and engineering.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advanced) repeater course in aldehydes and ketones is an important and rewarding course of study for students who are passionate about organic chemistry and want to succeed on the exam and pursue careers in the field.
Overview of JEE (Main+Advance) Repeater Course Aldehydes and Ketones
The JEE (Main+Advanced) repeater course in aldehydes and ketones is an important part of the organic chemistry syllabus and covers a wide range of topics related to these organic compounds. Here is an overview of the course:
- Introduction: The course begins with an introduction to aldehydes and ketones, including their general structure, nomenclature, and physical properties.
- Preparation: Students learn various methods for the preparation of aldehydes and ketones, including oxidation of alcohols, ozonolysis of alkenes, and Friedel-Crafts acylation.
- Properties and reactions: The course covers the properties of aldehydes and ketones, including their acidity, basicity, and reactivity towards nucleophiles and electrophiles. Students also learn about various reactions of aldehydes and ketones, including nucleophilic addition reactions, oxidation-reduction reactions, and condensation reactions.
- Stereochemistry: The course includes a discussion of the stereochemistry of aldehydes and ketones, including the concept of enantiomers and diastereomers and their optical activity.
- Applications: The course covers the applications of aldehydes and ketones in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, flavors, and fragrances. Students also learn about the role of aldehydes and ketones in the synthesis of important organic compounds, such as amino acids and carbohydrates.
Throughout the course, students are expected to solve practice problems and participate in group discussions to reinforce their understanding of the material. The course may also include laboratory experiments to give students hands-on experience with the preparation and reactions of aldehydes and ketones.
By the end of the course, students should have a solid understanding of aldehydes and ketones and be well-prepared to tackle related questions on the JEE (Main+Advanced) exam. They will also have developed critical thinking skills and problem-solving abilities that will be useful in many different areas of science and engineering.
Types of JEE (Main+Advance) Repeater Course Aldehydes and Ketones
There are different types of JEE (Main+Advanced) repeater courses in aldehydes and ketones, depending on the level of depth and focus on specific topics. Here are some examples:
- Comprehensive course: This type of course covers all the topics related to aldehydes and ketones in detail, including their preparation, properties, reactions, stereochemistry, and applications. It is suitable for students who want a thorough understanding of the subject and are aiming for a high score on the exam.
- Crash course: This type of course provides a condensed overview of the most important topics related to aldehydes and ketones. It is suitable for students who want to quickly review the material before the exam or for those who need a refresher on specific topics.
- Problem-solving course: This type of course focuses on solving practice problems related to aldehydes and ketones. It is suitable for students who want to improve their problem-solving skills and gain confidence in tackling different types of questions on the exam.
- Laboratory course: This type of course emphasizes hands-on laboratory experiments related to aldehydes and ketones. It is suitable for students who want to gain practical experience with the preparation and reactions of these compounds and learn about experimental techniques in organic chemistry.
- Specialized course: This type of course focuses on specific topics related to aldehydes and ketones, such as their use in pharmaceuticals, flavors, or materials science. It is suitable for students who are interested in pursuing a career in a particular field of organic chemistry and want to gain specialized knowledge in that area.
Overall, the type of JEE (Main+Advanced) repeater course in aldehydes and ketones that a student chooses will depend on their individual needs and goals for the exam and their future career aspirations.
Structures of JEE (Main+Advance) Repeater Course Aldehydes and Ketones
Aldehydes and ketones have a general structure that includes a carbonyl group, which consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom. The structure of aldehydes and ketones differs based on the substituents attached to the carbonyl carbon. Here are some examples of structures of aldehydes and ketones:
- Formaldehyde (methanal): HCHO
- Acetaldehyde (ethanal): CH3CHO
- Propanal: CH3CH2CHO
- Butanal: CH3CH2CH2CHO
- Benzaldehyde: C6H5CHO
- Acetone (2-propanone): (CH3)2CO
- Butanone (2-butanone): CH3CH2C(O)CH2CH3
- Cyclohexanone: C6H10O
In aldehydes, the carbonyl group is always at the end of a carbon chain, whereas in ketones, the carbonyl group is located within the carbon chain. The position of the carbonyl group in the molecule influences the physical and chemical properties of aldehydes and ketones, such as boiling point, solubility, and reactivity towards different types of reactions.
Application of JEE (Main+Advance) Repeater Course Aldehydes and Ketones
The JEE (Main+Advanced) repeater course in aldehydes and ketones has several applications in different fields. Here are some examples:
- Organic synthesis: Aldehydes and ketones are important building blocks in organic synthesis, and their preparation and reactions are essential for the synthesis of a wide range of organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials.
- Food and flavor industry: Many aldehydes and ketones are used in the food and flavor industry as flavoring agents, preservatives, and aroma enhancers. For example, vanillin, which is a major component of vanilla flavor, is a derivative of an aldehyde.
- Polymer chemistry: Aldehydes and ketones can also be used as monomers in polymer chemistry, where they are polymerized to form polymeric materials with specific properties. For example, polyacetal, which is a polymer of formaldehyde, is used in the production of gears, bearings, and other mechanical parts.
- Pharmaceuticals: Aldehydes and ketones are also used in the synthesis of many pharmaceuticals, such as antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and anti-inflammatory agents. For example, cortisone, which is used to treat inflammation, is synthesized from a ketone.
- Industrial processes: Aldehydes and ketones are used in many industrial processes, such as the production of solvents, resins, and plasticizers. For example, acetone, which is a common ketone, is used as a solvent in the production of plastics and resins.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advanced) repeater course in aldehydes and ketones has many applications in different fields, and understanding the preparation, properties, and reactions of these compounds is essential for a career in organic chemistry and related fields.
Nomenclature of JEE (Main+Advance) Repeater Course Aldehydes and Ketones
The nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones follows the rules set by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). The names of aldehydes and ketones are based on the longest carbon chain that contains the carbonyl group, and the suffix “-al” or “-one” is added depending on whether the compound is an aldehyde or a ketone, respectively. Here are some guidelines for naming aldehydes and ketones:
- Aldehydes: The parent chain is the longest carbon chain that contains the aldehyde functional group. The carbon atom of the aldehyde group is numbered as carbon 1, and the suffix “-al” is added to the stem name of the parent chain. If the aldehyde group is attached to a ring, the suffix “-carbaldehyde” is used instead. For example, HCHO is called formaldehyde, and CH3CHO is called acetaldehyde.
- Ketones: The parent chain is the longest carbon chain that contains the ketone functional group. The ketone group is located between two carbon atoms, which are numbered as carbons 1 and 2. The suffix “-one” is added to the stem name of the parent chain. If there are other functional groups present, the ketone group is numbered so that it receives the lowest possible number. For example, (CH3)2CO is called propanone.
- Common names: Some aldehydes and ketones have common names that are widely used. For example, formaldehyde (HCHO) is also known as methanal, and acetone ((CH3)2CO) is also known as propanone.
In addition to the basic rules for nomenclature, there are also specific rules for naming aldehydes and ketones with substituents, as well as naming cyclic aldehydes and ketones. A thorough understanding of nomenclature is important for understanding the properties and reactions of aldehydes and ketones.
Career Opportunities of JEE (Main+Advance) Repeater Course Aldehydes and Ketones
The JEE (Main+Advance) repeater course in aldehydes and ketones can lead to various career opportunities in different fields, including:
- Chemical industry: Aldehydes and ketones are essential building blocks for many organic compounds, and as such, there are many job opportunities in the chemical industry, such as pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science. Organic chemists with expertise in aldehydes and ketones can work in research and development, process development, and quality control.
- Flavor and fragrance industry: Aldehydes and ketones are important flavoring and fragrance agents in the food and cosmetic industries. Organic chemists with expertise in aldehydes and ketones can work in the development and production of these products, as well as in quality control and regulatory affairs.
- Academic research: Organic chemists with expertise in aldehydes and ketones can also work in academic research, where they can investigate the properties and reactions of these compounds, as well as develop new synthetic methods.
- Government and regulatory agencies: Organic chemists with expertise in aldehydes and ketones can work in government agencies responsible for regulating the production and use of chemicals, such as the Environmental Protection Agency and the Food and Drug Administration.
- Patent law: Organic chemists with expertise in aldehydes and ketones can work as patent attorneys or patent agents, where they can use their knowledge to help clients protect their intellectual property.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advance) repeater course in aldehydes and ketones can lead to many career opportunities in different fields, and a thorough understanding of the properties and reactions of these compounds is essential for success in these careers.
