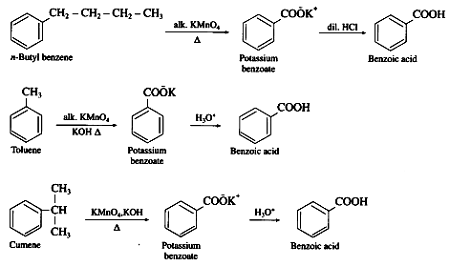
Benzoic acid can be prepared from alkylbenzenes by the following steps:
- Oxidation: The first step is the oxidation of alkylbenzenes to form benzoic acid. This can be achieved by using either hot concentrated nitric acid or potassium permanganate in the presence of sulfuric acid. The reaction is as follows:R-C6H5 + 3O2 → PhCOOH + H2O
- Acidification: The resulting product from step 1 is a mixture of benzoic acid and unreacted starting material. The next step is to acidify the mixture by adding dilute hydrochloric acid. This converts any remaining alkylbenzenes into their corresponding benzoic acid.
- Extraction: The benzoic acid is extracted from the mixture using a solvent such as ether or dichloromethane. The solvent is added to the mixture and the two layers are separated. The benzoic acid is present in the aqueous layer while the solvent layer contains impurities and unreacted starting material.
- Purification: The final step is to purify the benzoic acid by recrystallization. The benzoic acid is dissolved in a hot solvent and then allowed to cool slowly, causing the benzoic acid to crystallize out of the solution. The crystals are then collected by filtration and washed with cold solvent to remove any impurities.
Overall, the process involves oxidation of the starting material, followed by acidification, extraction and purification to obtain pure benzoic acid.
What is Required Preparation of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes
To prepare benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes, you will need the following materials:
- Alkylbenzene: This can be any alkyl-substituted benzene, such as toluene or ethylbenzene.
- Oxidizing agent: You will need an oxidizing agent to convert the alkyl group on the benzene ring to a carboxylic acid group. Examples of suitable oxidizing agents include hot concentrated nitric acid or potassium permanganate in the presence of sulfuric acid.
- Hydrochloric acid: Dilute hydrochloric acid is used to acidify the reaction mixture after the oxidation step to convert any remaining alkylbenzenes into their corresponding benzoic acid.
- Solvent: A solvent such as ether or dichloromethane is needed to extract the benzoic acid from the reaction mixture. The solvent will dissolve the benzoic acid, leaving behind impurities and unreacted starting material.
- Water: Water is needed to wash the benzoic acid crystals after recrystallization to remove any remaining impurities.
- Glassware and equipment: You will need standard laboratory glassware and equipment such as a round-bottom flask, condenser, separatory funnel, and vacuum filtration apparatus.
- Safety equipment: As with any laboratory work, you will need to wear appropriate safety equipment such as gloves, safety glasses, and a lab coat to protect yourself from chemicals and other hazards.
When is Required Preparation of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes
The preparation of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes is typically carried out in a laboratory setting by organic chemists. This reaction may be performed as part of a synthesis of a larger organic molecule or simply to obtain pure benzoic acid for further experimentation or analysis. The reaction is typically carried out under controlled conditions using appropriate safety measures and equipment.
There are also industrial methods for producing benzoic acid from toluene, which involves a series of chemical reactions using specialized equipment and conditions. These methods are used to produce large quantities of benzoic acid for commercial use in a variety of applications, including as a food preservative and a precursor for the production of other organic compounds.
Where is Required Preparation of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes
The preparation of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes is typically carried out in a laboratory setting, such as in an organic chemistry research laboratory at a university or a chemical company. The laboratory will have specialized equipment and chemicals required to carry out the reaction safely and effectively.
Industrial production of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes is typically carried out in chemical plants that specialize in the production of organic chemicals. These plants are usually located near sources of raw materials and transportation infrastructure for shipping the finished products. The production process involves specialized equipment and trained personnel to operate the machinery and ensure the safe handling of the chemicals involved.
How is Required Preparation of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes
The preparation of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes typically involves the following steps:
- Oxidation: The first step is the oxidation of the alkylbenzene using an oxidizing agent such as hot concentrated nitric acid or potassium permanganate in the presence of sulfuric acid. This converts the alkyl group on the benzene ring to a carboxylic acid group, forming benzoic acid.
- Acidification: The resulting mixture from step 1 is a mixture of benzoic acid and unreacted starting material. Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to the mixture to acidify it, which converts any remaining alkylbenzenes into their corresponding benzoic acid.
- Extraction: The benzoic acid is then extracted from the mixture using a solvent such as ether or dichloromethane. The solvent is added to the mixture, and the two layers are separated. The benzoic acid is present in the aqueous layer while the solvent layer contains impurities and unreacted starting material.
- Purification: The final step is to purify the benzoic acid by recrystallization. The benzoic acid is dissolved in a hot solvent and then allowed to cool slowly, causing the benzoic acid to crystallize out of the solution. The crystals are then collected by filtration and washed with cold solvent to remove any impurities.
Overall, the reaction involves converting the alkyl group on the benzene ring to a carboxylic acid group by oxidation, followed by acidification, extraction and purification to obtain pure benzoic acid.
Structures of Preparation of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes
The preparation of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes involves the conversion of the alkyl group on the benzene ring to a carboxylic acid group. The reaction mechanism and structures involved can be illustrated as follows:
Step 1: Oxidation R-Ph + KMnO4 + H2SO4 → PhCOOH + K2SO4 + MnSO4 + H2O
In this step, an oxidizing agent such as potassium permanganate (KMnO4) or hot concentrated nitric acid is used to oxidize the alkyl group on the benzene ring to a carboxylic acid group, forming benzoic acid (PhCOOH) and other products.
Step 2: Acidification PhCOOH + HCl → PhCOOH2+ + Cl-
In this step, dilute hydrochloric acid is used to acidify the reaction mixture, which converts any remaining alkylbenzenes into their corresponding benzoic acid.
Step 3: Extraction PhCOOH2+ + CH2Cl2 → PhCOOH(CH2Cl2) + H+
In this step, a solvent such as dichloromethane is used to extract the benzoic acid from the reaction mixture. The solvent dissolves the benzoic acid, leaving behind impurities and unreacted starting material in the aqueous layer.
Step 4: Purification PhCOOH(CH2Cl2) → PhCOOH(s) + CH2Cl2
In the final step, the benzoic acid is purified by recrystallization. The benzoic acid is dissolved in hot solvent such as water or ethanol and then allowed to cool slowly, causing the benzoic acid to crystallize out of the solution. The crystals are then collected by filtration and washed with cold solvent to remove any impurities. The final product is pure benzoic acid in the form of white crystalline solid.
Case Study on Preparation of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes
Preparation of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes involves the conversion of alkylbenzenes to benzoic acid. This process involves several steps, including oxidation, cleavage, and carboxylation. The following is a case study on the preparation of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes.
Step 1: Oxidation
In the first step, the alkylbenzene is oxidized using a strong oxidizing agent such as potassium permanganate (KMnO4) or chromic acid (H2CrO4). The oxidation process converts the alkyl group to a carboxylic acid group, which is a necessary intermediate for the preparation of benzoic acid.
Step 2: Cleavage
After the oxidation, the cleavage of the intermediate carboxylic acid group from the alkyl chain is performed by acidic hydrolysis using hydrochloric acid (HCl) or sulfuric acid (H2SO4) at elevated temperatures. The cleavage results in the formation of a benzoic acid derivative known as a benzyl carboxylic acid.
Step 3: Carboxylation
In the final step, carboxylation is performed to convert the benzyl carboxylic acid to benzoic acid. This is done by treating the benzyl carboxylic acid with a strong base such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and carbon dioxide (CO2) at elevated temperatures and pressure. The reaction results in the formation of benzoic acid and sodium benzoate (NaC7H5O2).
Overall Reaction:
The overall reaction for the preparation of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes is as follows:
R-C6H5 + 2 KMnO4 + 3 H2SO4 → R-COOH + CO2 + MnSO4 + K2SO4 + 3 H2O
R-COOH + H2O → R-C6H5COOH
R-C6H5COOH + NaOH + CO2 → NaC7H5O2 + H2O + C6H5COOH
NaC7H5O2 + HCl → C6H5COOH + NaCl
Overall, the preparation of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes is a complex process that requires careful attention to detail and safety precautions due to the use of strong oxidizing agents and acids. The final product is a versatile compound used in the production of various chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
White paper on Preparation of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes
Introduction
Benzoic acid is a widely used organic acid with a broad range of applications in the food, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical industries. It is also an essential building block for the production of various chemicals, such as phenol, caprolactam, and benzyl alcohol. One of the most common methods for preparing benzoic acid is the conversion of alkylbenzenes, which are readily available and inexpensive, to benzoic acid. This white paper describes the preparation of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes through a series of chemical reactions.
Preparation of Benzoic Acid from Alkylbenzenes
The preparation of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes involves three main steps: oxidation, cleavage, and carboxylation. The overall reaction can be represented as follows:
R-C6H5 + 2 KMnO4 + 3 H2SO4 → R-COOH + CO2 + MnSO4 + K2SO4 + 3 H2O
R-COOH + H2O → R-C6H5COOH
R-C6H5COOH + NaOH + CO2 → NaC7H5O2 + H2O + C6H5COOH
NaC7H5O2 + HCl → C6H5COOH + NaCl
Step 1: Oxidation
In the first step, the alkylbenzene is oxidized to form an intermediate carboxylic acid group. The most commonly used oxidizing agents are potassium permanganate (KMnO4) and chromic acid (H2CrO4). The oxidation reaction occurs at elevated temperatures in the presence of sulfuric acid (H2SO4). The reaction yields the corresponding carboxylic acid as shown in the first reaction above.
Step 2: Cleavage
After oxidation, the intermediate carboxylic acid group is cleaved from the alkyl chain by acidic hydrolysis using hydrochloric acid (HCl) or sulfuric acid (H2SO4) at elevated temperatures. The cleavage reaction results in the formation of a benzoic acid derivative known as a benzyl carboxylic acid, as shown in the second reaction above.
Step 3: Carboxylation
In the final step, carboxylation is performed to convert the benzyl carboxylic acid to benzoic acid. This is done by treating the benzyl carboxylic acid with a strong base such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and carbon dioxide (CO2) at elevated temperatures and pressure. The reaction results in the formation of benzoic acid and sodium benzoate (NaC7H5O2) as shown in the third reaction above.
After carboxylation, the final product is purified by precipitation, filtration, and recrystallization.
Conclusion
The preparation of benzoic acid from alkylbenzenes is a complex process that requires careful attention to detail and safety precautions due to the use of strong oxidizing agents and acids. The process involves three main steps: oxidation, cleavage, and carboxylation. The final product is a versatile compound used in the production of various chemicals and pharmaceuticals. The process is an economically viable method for producing benzoic acid from readily available and inexpensive starting materials.