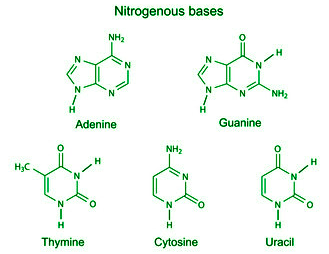
Nucleic acids: Chemical composition
Nucleic acids are macromolecules that are essential to all living organisms. They are made up of building blocks called nucleotides, which consist of a nitrogenous base, a sugar molecule, and a phosphate group. There are two types of nucleic acids: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The chemical composition of DNA nucleotides includes: The…