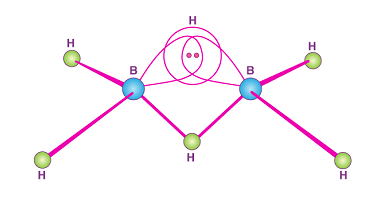
Group 16 Reactivity towards hydrogen
Group 16 elements, also known as the chalcogens, have varying reactivities towards hydrogen. Oxygen (O) and sulfur (S) are non-metals and tend to form covalent bonds with hydrogen. Oxygen can form water (H2O) with hydrogen, while sulfur can form hydrogen sulfide (H2S) or sulfuric acid (H2SO4) depending on the reaction conditions. On the other hand,…