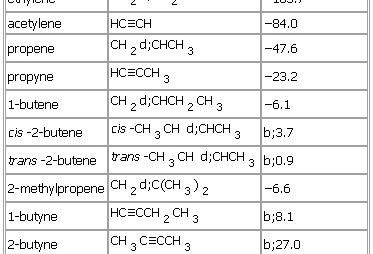
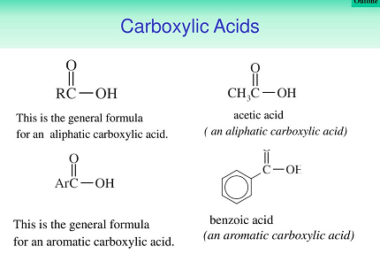
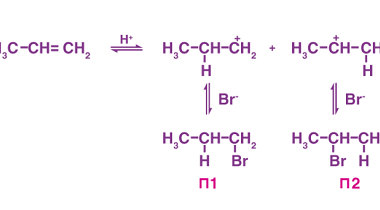
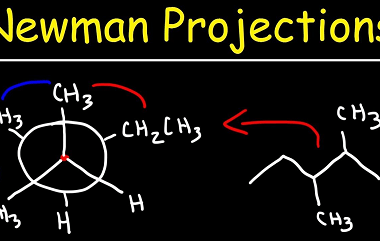
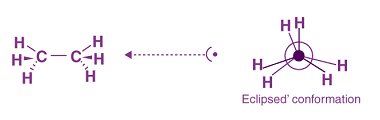
Physical properties (boiling points)
Boiling point is a physical property of a substance that refers to the temperature at which the substance changes from a liquid state to a gaseous state. It is determined by the strength of intermolecular forces within the substance and the atmospheric pressure. Some examples of boiling points of common substances are: It’s worth noting…