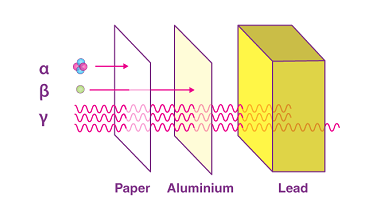
Thin lenses
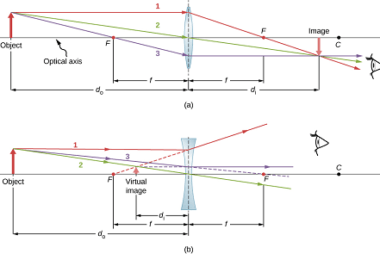
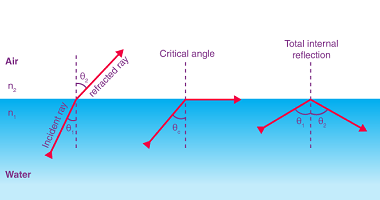
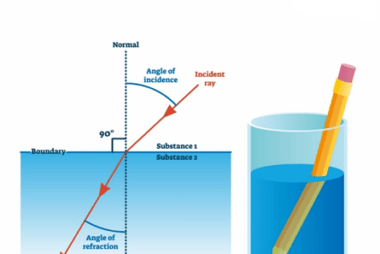
A thin lens is a lens with a thickness much smaller than its focal length. It is a simple optical device that can be used to bend or focus light, and is commonly used in various optical systems, such as cameras, microscopes, telescopes, and eyeglasses. There are two types of thin lenses: convex and concave.…