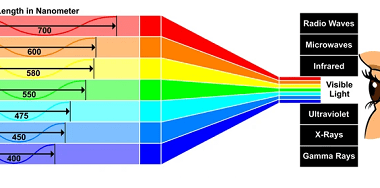
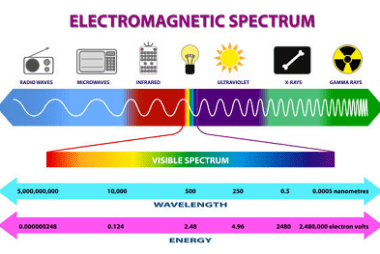
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) refers to electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light but longer than X-rays. It is typically divided into three categories based on wavelength: UV-A (400-320 nm), UV-B (320-280 nm), and UV-C (280-100 nm). UV radiation is produced by the sun and is also used in various industrial and medical…