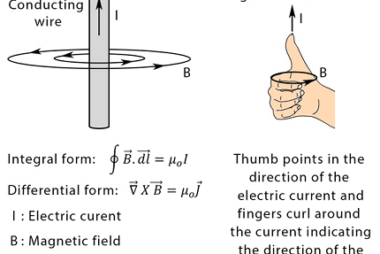
Magnetic field near a current-carrying straight wire
When an electric current flows through a straight wire, it creates a magnetic field around the wire. This magnetic field is known as the “magnetic field near a current-carrying straight wire.” The magnetic field is perpendicular to the wire and its direction is given by the right-hand rule. If you point your right thumb in…